Kubernetes Components
Architecture
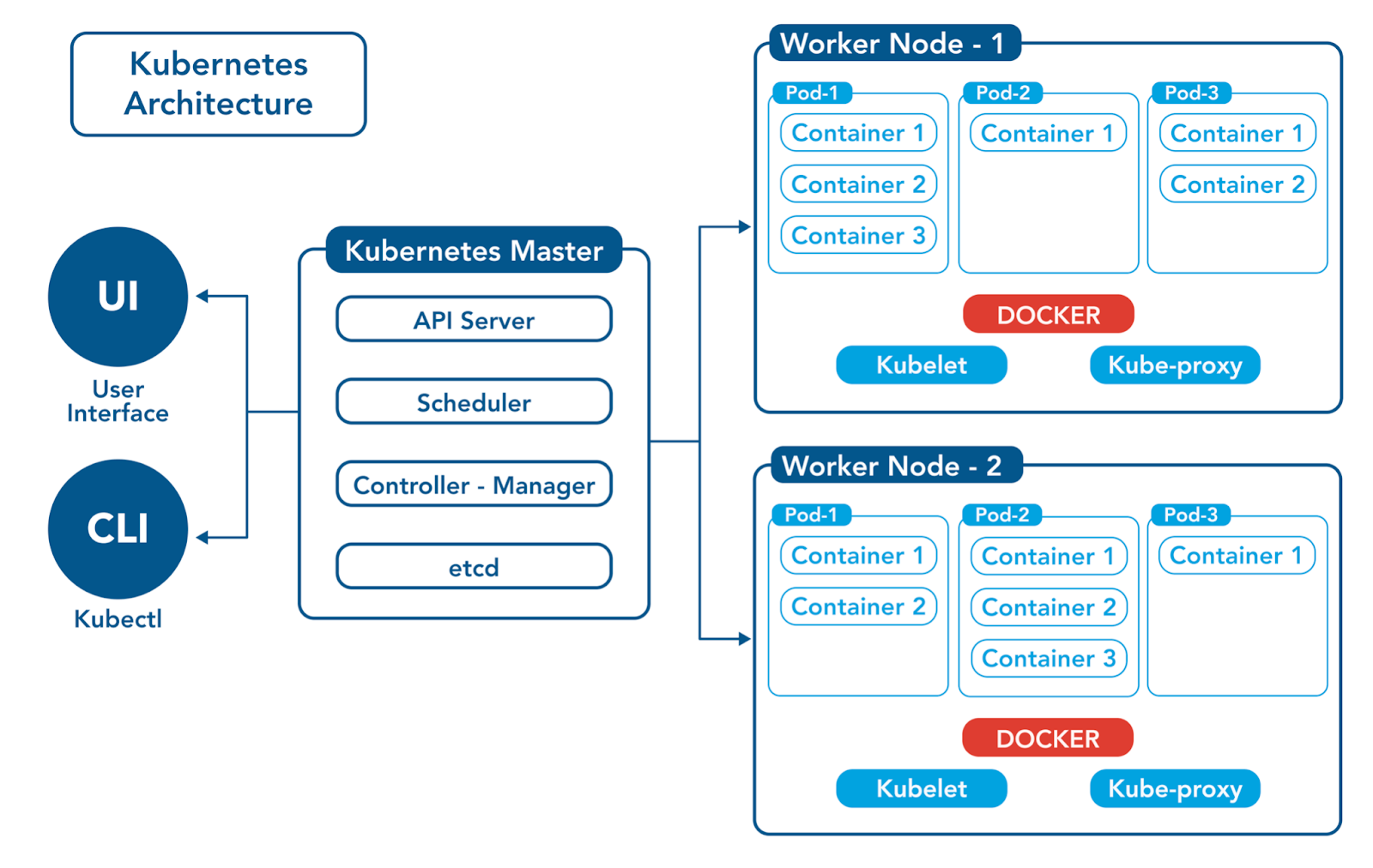
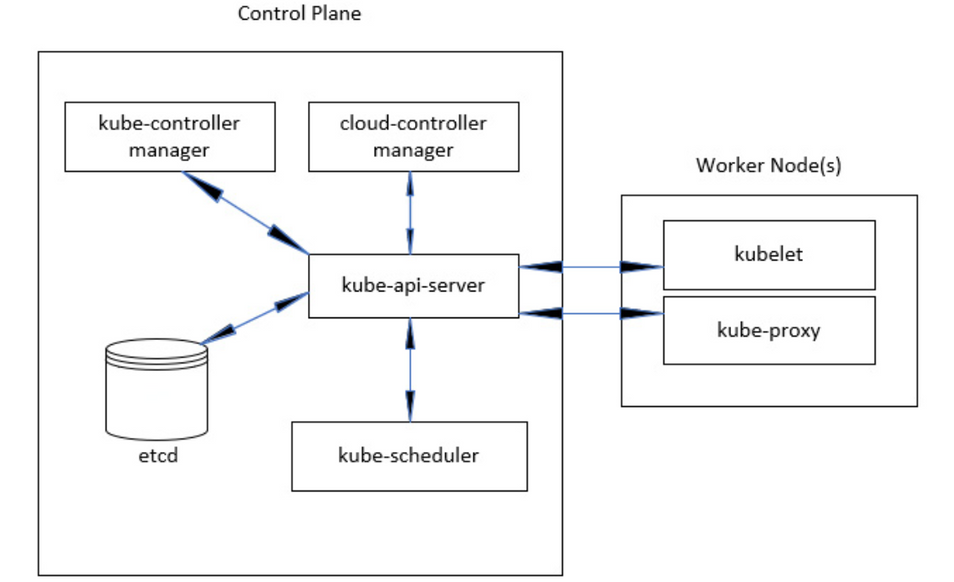
Master Node Components
The master components of Kubernetes are responsible for managing the overall state of the cluster. It orchestrates the deployment and scaling of containerized applications. The master components include:
API Server
The API server is the central management entity of Kubernetes. It serves all the RESTful API calls that are made to the cluster. It is responsible for validating and processing API requests and updating the state of the cluster.
etcd
etcd is a distributed key-value store that is used to store the configuration data of the cluster. It is used as the backing store for all cluster data.
Controller Manager
The controller manager is responsible for managing various controllers that regulate the state of the cluster. It ensures that the desired state of the cluster matches the actual state.
Scheduler
The scheduler is responsible for scheduling the deployment of containers on the worker nodes. It selects the best node for a given pod and ensures that the required resources are available before scheduling the pod.
Worker Node Components
The node components run on each worker node in the cluster. They are responsible for managing the containers and the associated resources on the node. The node components include:
Kubelet
Kubelet is the primary agent that runs on each worker node. It is responsible for managing the state of the containers running on the node. It communicates with the API server to receive instructions on which containers to run and ensures that the containers are healthy.
kube-proxy
kube-proxy is responsible for managing the network connectivity between different pods and services in the cluster. It ensures that each pod can communicate with other pods and external services.
Container Runtime
The container runtime is responsible for running the containers. Kubernetes supports various container runtimes, including Docker, containerd, and CRI-O.
| Component name | Control plane, worker node, or client |
|---|---|
| Kubeadm | Admin tool |
| Kube-apiserver | Control plane (master node) |
| Etcd | Control plane (master node) |
| Kube-scheduler | Control plane (master node) |
| Kube-controller-manager | Control plane (master node) |
| Kubelet | Worker node |
| Kube-proxy | Worker node |
| Container Engine | Worker node |
| kubectl | Client |
Interacting with the API server
- CLI: kubectl
- API:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/kubernetes-api
kubectl & kubeadm
kubectl create
kubectl get
kubectl apply
kubectl describe
kubectl exec
kubectl run
kubeadm config
kubeadm init
kubeadm join
kubeadm reset
API Resources Shortname
| NAME | SHORTNAMES |
|---|---|
| configmaps | cm |
| endpoints | ep |
| events | ev |
| namespaces | ns |
| nodes | no |
| persistentvolumeclaims | pvc |
| persistentvolumes | pv |
| pods | po |
| replicationcontrollers | rc |
| serviceaccounts | sa |
| services | svc |
| daemonsets | ds |
| deployments | deploy |
| replicasets | rs |
| cronjobs | cj |
| networkpolicies | netpol |
| podsecuritypolicies | psp |
API Resources List
kubectl api-resources --sort-by name -o wide
| NAME | SHORTNAMES | APIVERSION | NAMESPACED | KIND |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bindings | v1 | TRUE | Binding | |
| componentstatuses | cs | v1 | FALSE | ComponentStatus |
| configmaps | cm | v1 | TRUE | ConfigMap |
| endpoints | ep | v1 | TRUE | Endpoints |
| events | ev | v1 | TRUE | Event |
| limitranges | limits | v1 | TRUE | LimitRange |
| namespaces | ns | v1 | FALSE | Namespace |
| nodes | no | v1 | FALSE | Node |
| persistentvolumeclaims | pvc | v1 | TRUE | PersistentVolumeClaim |
| persistentvolumes | pv | v1 | FALSE | PersistentVolume |
| pods | po | v1 | TRUE | Pod |
| podtemplates | v1 | TRUE | PodTemplate | |
| replicationcontrollers | rc | v1 | TRUE | ReplicationController |
| resourcequotas | quota | v1 | TRUE | ResourceQuota |
| secrets | v1 | TRUE | Secret | |
| serviceaccounts | sa | v1 | TRUE | ServiceAccount |
| services | svc | v1 | TRUE | Service |
| mutatingwebhookconfigurations | admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1 | FALSE | MutatingWebhookConfiguration | |
| validatingwebhookconfigurations | admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1 | FALSE | ValidatingWebhookConfiguration | |
| customresourcedefinitions | crd,crds | apiextensions.k8s.io/v1 | FALSE | CustomResourceDefinition |
| apiservices | apiregistration.k8s.io/v1 | FALSE | APIService | |
| controllerrevisions | apps/v1 | TRUE | ControllerRevision | |
| daemonsets | ds | apps/v1 | TRUE | DaemonSet |
| deployments | deploy | apps/v1 | TRUE | Deployment |
| replicasets | rs | apps/v1 | TRUE | ReplicaSet |
| statefulsets | sts | apps/v1 | TRUE | StatefulSet |
| tokenreviews | authentication.k8s.io/v1 | FALSE | TokenReview | |
| localsubjectaccessreviews | authorization.k8s.io/v1 | TRUE | LocalSubjectAccessReview | |
| selfsubjectaccessreviews | authorization.k8s.io/v1 | FALSE | SelfSubjectAccessReview | |
| selfsubjectrulesreviews | authorization.k8s.io/v1 | FALSE | SelfSubjectRulesReview | |
| subjectaccessreviews | authorization.k8s.io/v1 | FALSE | SubjectAccessReview | |
| horizontalpodautoscalers | hpa | autoscaling/v2 | TRUE | HorizontalPodAutoscaler |
| cronjobs | cj | batch/v1 | TRUE | CronJob |
| jobs | batch/v1 | TRUE | Job | |
| certificatesigningrequests | csr | certificates.k8s.io/v1 | FALSE | CertificateSigningRequest |
| leases | coordination.k8s.io/v1 | TRUE | Lease | |
| bgpconfigurations | crd.projectcalico.org/v1 | FALSE | BGPConfiguration | |
| bgppeers | crd.projectcalico.org/v1 | FALSE | BGPPeer | |
| blockaffinities | crd.projectcalico.org/v1 | FALSE | BlockAffinity | |
| caliconodestatuses | crd.projectcalico.org/v1 | FALSE | CalicoNodeStatus | |
| clusterinformations | crd.projectcalico.org/v1 | FALSE | ClusterInformation | |
| felixconfigurations | crd.projectcalico.org/v1 | FALSE | FelixConfiguration | |
| globalnetworkpolicies | crd.projectcalico.org/v1 | FALSE | GlobalNetworkPolicy | |
| globalnetworksets | crd.projectcalico.org/v1 | FALSE | GlobalNetworkSet | |
| hostendpoints | crd.projectcalico.org/v1 | FALSE | HostEndpoint | |
| ipamblocks | crd.projectcalico.org/v1 | FALSE | IPAMBlock | |
| ipamconfigs | crd.projectcalico.org/v1 | FALSE | IPAMConfig | |
| ipamhandles | crd.projectcalico.org/v1 | FALSE | IPAMHandle | |
| ippools | crd.projectcalico.org/v1 | FALSE | IPPool | |
| ipreservations | crd.projectcalico.org/v1 | FALSE | IPReservation | |
| kubecontrollersconfigurations | crd.projectcalico.org/v1 | FALSE | KubeControllersConfiguration | |
| networkpolicies | crd.projectcalico.org/v1 | TRUE | NetworkPolicy | |
| networksets | crd.projectcalico.org/v1 | TRUE | NetworkSet | |
| endpointslices | discovery.k8s.io/v1 | TRUE | EndpointSlice | |
| events | ev | events.k8s.io/v1 | TRUE | Event |
| flowschemas | flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta3 | FALSE | FlowSchema | |
| prioritylevelconfigurations | flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta3 | FALSE | PriorityLevelConfiguration | |
| ingressclasses | networking.k8s.io/v1 | FALSE | IngressClass | |
| ingresses | ing | networking.k8s.io/v1 | TRUE | Ingress |
| networkpolicies | netpol | networking.k8s.io/v1 | TRUE | NetworkPolicy |
| runtimeclasses | node.k8s.io/v1 | FALSE | RuntimeClass | |
| poddisruptionbudgets | pdb | policy/v1 | TRUE | PodDisruptionBudget |
| clusterrolebindings | rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 | FALSE | ClusterRoleBinding | |
| clusterroles | rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 | FALSE | ClusterRole | |
| rolebindings | rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 | TRUE | RoleBinding | |
| roles | rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 | TRUE | Role | |
| priorityclasses | pc | scheduling.k8s.io/v1 | FALSE | PriorityClass |
| csidrivers | storage.k8s.io/v1 | FALSE | CSIDriver | |
| csinodes | storage.k8s.io/v1 | FALSE | CSINode | |
| csistoragecapacities | storage.k8s.io/v1 | TRUE | CSIStorageCapacity | |
| storageclasses | sc | storage.k8s.io/v1 | FALSE | StorageClass |
| volumeattachments | storage.k8s.io/v1 | FALSE | VolumeAttachment |
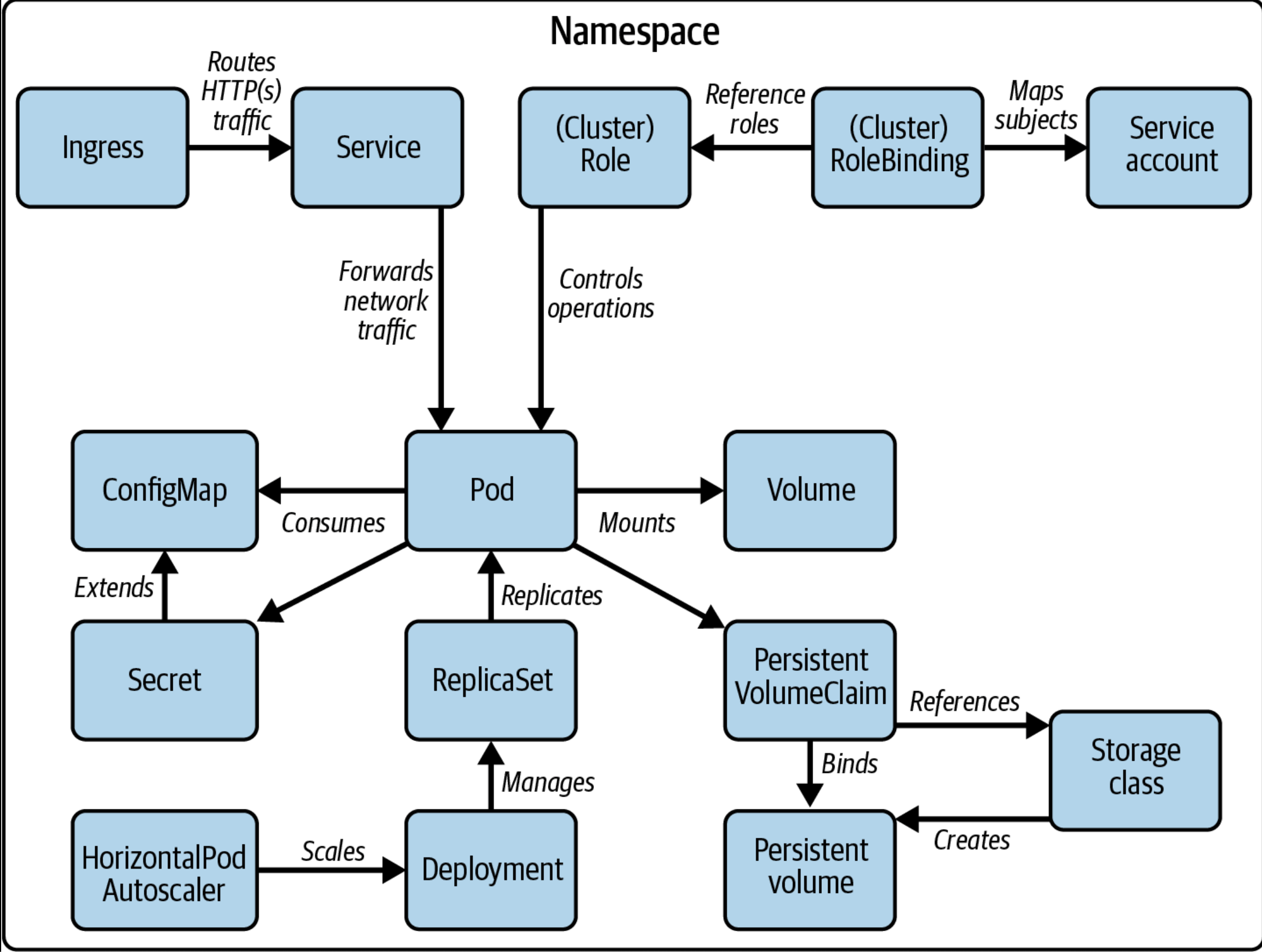
Components at a glance
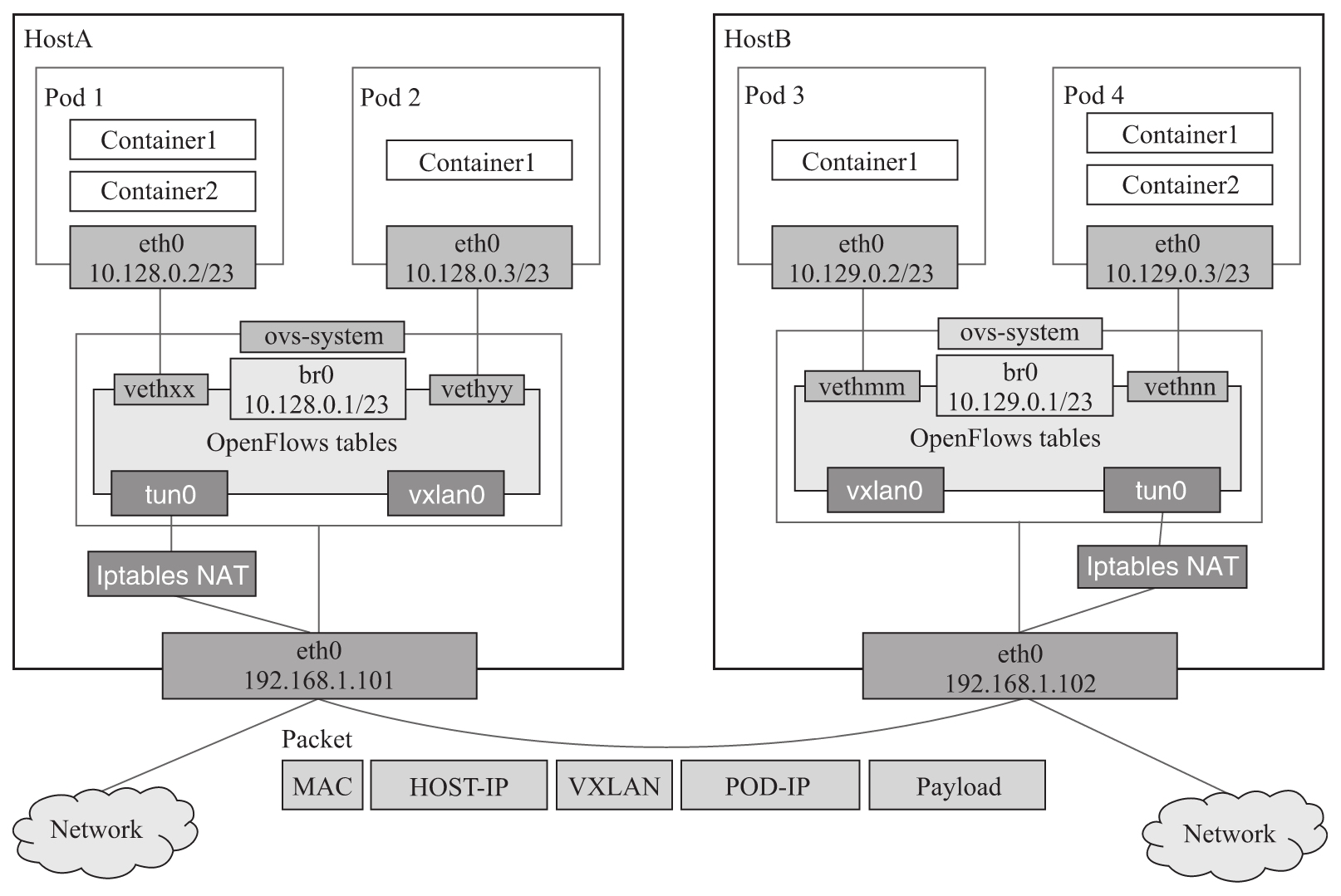
Network at a glance
Kubernetes Terminology
- Cluster: A group of connected computers (nodes) that run applications.
- Node: A single computer in a cluster that runs applications.
- Pod: The smallest unit in Kubernetes that can run one or more containers.
- Namespace: A way to divide resources in a cluster for dfferent projects or teams.
- Deployment: Manages a set of identical pods to ensure the correct number are running.
- ReplicaSet: Ensures a specified number of pod copies are running at all times.
- DaemonSet: Ensures a pod runs on all or some nodes.
- StatefulSet: Manages stateful applications, keeping track of each pod’s identity.
- Job: Runs a task until it completes successfully.
- CronJob: Runs tasks on a scheduled basis, like a cron job in Unix.
- Service: Exposes a set of pods as a network service.
- Ingress: Manages external access to services, usually HTTP .
- ConfigMap: Stores configuration data as key-value pairs.
- Secret: Stores sensitive data, like passwords and tokens.
- Volume: Provides storage for containers.
- PersistentVolume (PV): A piece of storage that an administrator sets up.
- PersistentVolumeClaim (PVC): A request for storage by a user.
- Kubelet: The agent that runs on each node to manage pods.
- Kube-Proxy: Manages network rules on nodes.
- Controller Manager: Manages controllers that regulate the state of the cluster.
- Scheduler: Decides which nodes will run new pods.
- Etcd: A key-value store that stores all cluster data.
- Kubectl: The command-line tool to interact with the Kubernetes API.
- Helm: A package manager for Kubernetes applications.
- Label: Key-value pairs attached to objects for organizing and selecting them.
- Annotation: Metadata attached to objects to provide additional information.
- Taints: Prevents specific pods from running on certain nodes.
- Tolerations: Allows pods to run on nodes with specific taints.
- Affnity/Anti-Affnity: Rules that specify which nodes can or cannot run specific pods.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Manages who can do what in the cluster.
- ServiceAccount: An identity for processes running in pods to interact with the Kubernetes API.
- ClusterRole: Defines permissions that apply across the entire cluster.
- Role: Defines permissions within a specific namespace.
- NetworkPolicy: Controls the traffc between pods in the cluster.
- PodSecurityPolicy: Defines security rules that pods must follow.
- PodDisruptionBudget (PDB): Limits the number of pods that can be unavailable during maintenance.
- Ingress Controller: Manages Ingress resources to provide HTTP and HTTPS routing.
- CoreDNS: A DNS server for the cluster, providing name resolution for services.
- StorageClass: Describes different types of storage available in the cluster.
- Init Containers: Special containers that run before the main containers in a pod start.
- Sidecar Container: A helper container that runs alongside the main container in a pod.
- Readiness Probe: Checks if a container is ready to start accepting traffc.
- Liveness Probe: Checks if a container is still running and should be restarted if not.
- Headless Service: A service without a cluster IP , used to directly access pods.
- LoadBalancer Service: Exposes a service externally using a cloud provider’s load balancer.
- ClusterIP Service: Exposes a service internally within the cluster.
- NodePort Service: Exposes a service on a static port on each node.
- Endpoints: A list of IP addresses and ports that a service forwards traffc to.
- Resource Quotas: Limits the amount of resources a namespace can use.
- LimitRange: Defines resource usage limits for containers in a namespace.
- Finalizer: Ensures that specific cleanup steps are completed before an object is deleted.
- Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA): Automatically scales the number of pods based on CPU/memory usage.
- Vertical Pod Autoscaler (VPA): Adjusts the resource limits and requests for running pods.
- Cluster Autoscaler: Automatically adjusts the size of the Kubernetes cluster by adding or removing nodes.
- Affnity Rules: Specify rules about which nodes can host a pod.
- Anti-Affnity Rules: Specify rules about which nodes should not host a pod.
- Init Containers: Special containers that run before the main containers in a pod start.
- Resource Requests: Specify the minimum amount of resources a container needs.
- Resource Limits: Specify the maximum amount of resources a container can use.
- PersistentVolumeClaim (PVC): A request for storage by a user.
- EmptyDir: A temporary directory that is created when a pod is assigned to a node.
- Security Context: Defines security settings for a pod or container.
- ServiceAccount: Provides an identity for processes running in pods.
- ClusterRoleBinding: Binds a ClusterRole to a user or group for the entire cluster.
- RoleBinding: Binds a Role to a user or group within a namespace.
- Pod Preset: Injects certain information, like secrets or volume mounts, into pods at creation.
- Priority Class: Specifies the priority of pods to influence their scheduling.
- Self-healing: Automatically replaces and reschedules failed containers.
- Secrets Management: Manages sensitive information like passwords and API keys.
- Default Namespace: The default namespace for Kubernetes objects without a specified namespace.
- Master Node: Controls and manages the Kubernetes cluster.
- Worker Node: Runs applications and workloads in pods.
- Helm Chart: Pre-configured Kubernetes resources packaged for easy deployment.
- Kustomize: Tool for customizing Kubernetes YAML configurations.
- Admission Controller: Intercepts requests to the Kubernetes API for validation and mutation.
- Custom Resource Definition (CRD): Extends Kubernetes by defining custom resources.
- Operator: Custom controllers for managing complex applications.
- Kubeadm: Tool for initializing and managing Kubernetes clusters.
- Minikube: Tool for running a single-node Kubernetes cluster locally for testing and development.
Reference
- Kubernetes – An Enterprise Guide (Marc Boorshtein, Scott Surovich)
- Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA) Study Guide (Benjamin Muschko)
https://argo-cd.readthedocs.io/en/stable/understand_the_basics/https://medium.com/@iam.ddsharma/kubernetes-at-a-glance-and-a-quick-cluster-deployment-70202a3c645ahttps://www.dynatrace.com/news/blog/kubernetes-health-at-a-glance-one-experience-to-rule-it-all/https://www.appvia.io/blog/intro-guide-to-kuberneteshttps://kubernetes.io/blog/2024/03/12/kubernetes-1-30-upcoming-changes/https://kublr.com/media/under-the-hood-an-introduction-to-kubernetes-architecture-2/https://mvallim.github.io/kubernetes-under-the-hood/documentation/kube-overview.html
Some of the content is generated by AI, please be cautious in identifying it.