What is DNS
Introduction
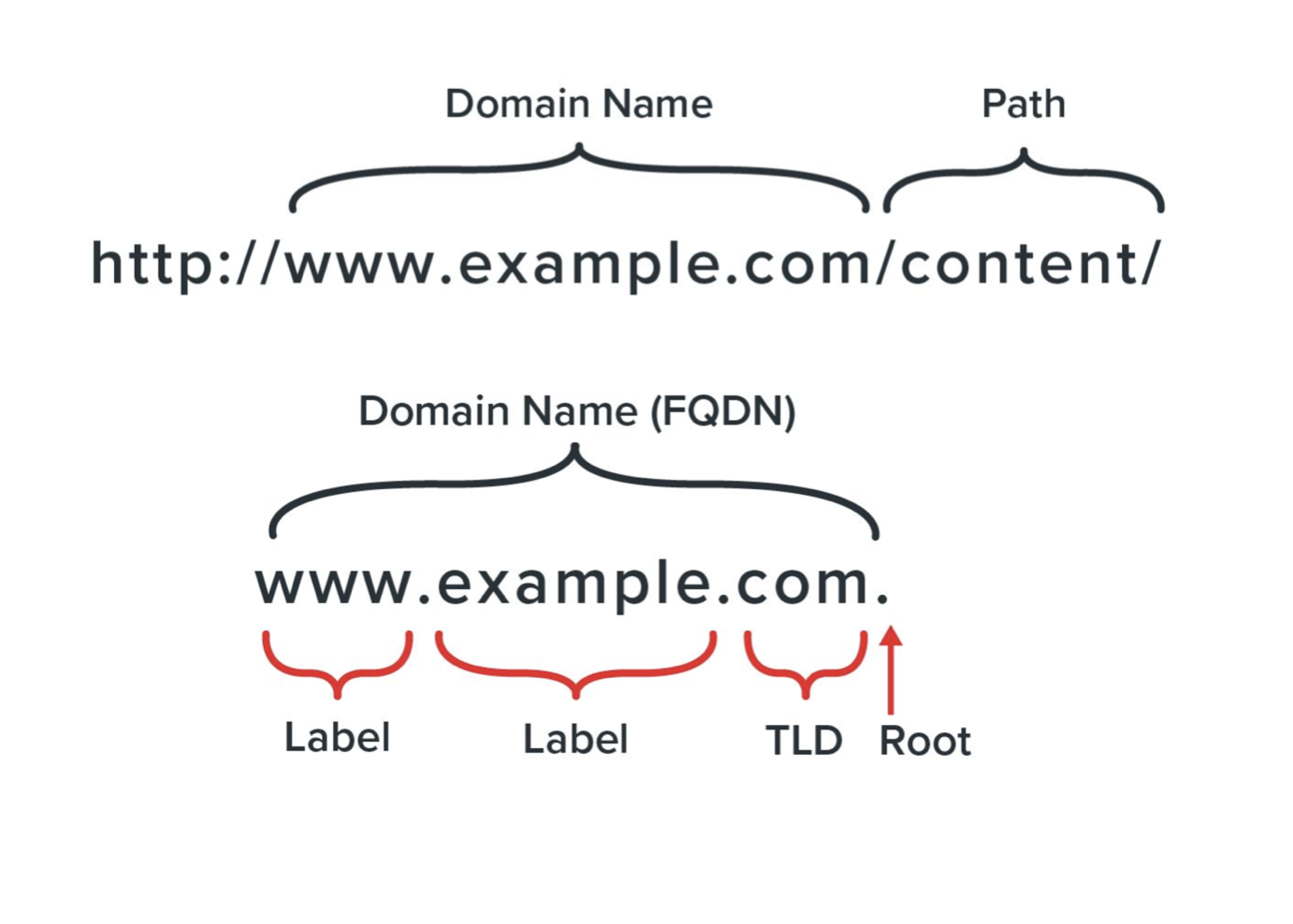
DNS stands for Domain Name System. It is a hierarchical naming system that maps domain names to IP addresses. DNS plays a crucial role in the functioning of the internet. In this 30 minutes guide, we will discuss the basics of DNS and how it works.
How DNS Works
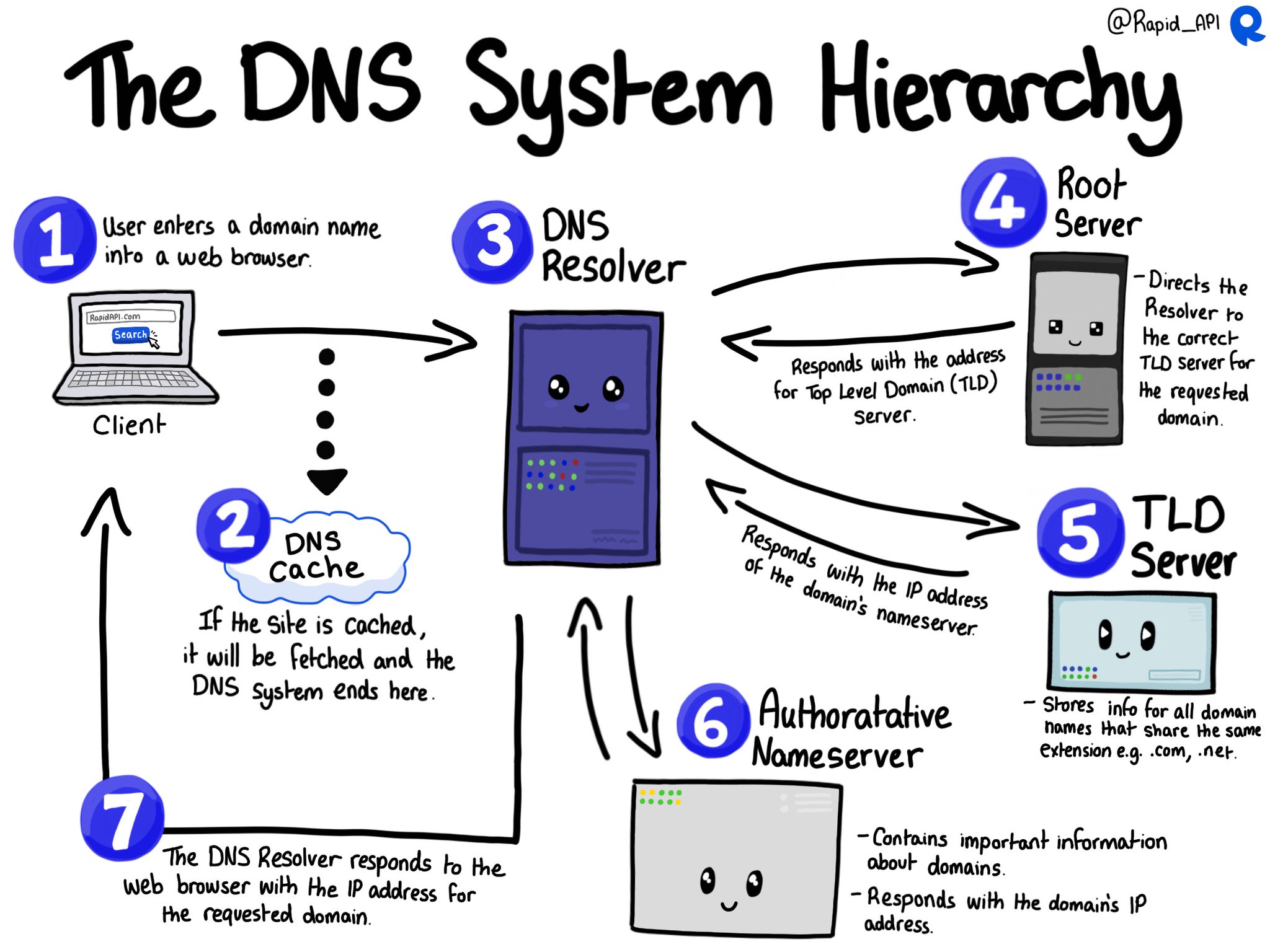
When you type a URL into your web browser, it sends a request to a DNS resolver to map the domain name to an IP address. The resolver checks its cache to see if it has the IP address for the domain name. If it doesn’t, the resolver sends a request to a DNS root server. The root server responds with the IP address of the top-level domain server that manages the domain name’s extension.
The resolver then sends a request to the top-level domain server, which responds with the IP address of the authoritative name server for the domain name. The authoritative name server has the IP address for the domain name and responds with it to the resolver. The resolver caches the IP address and sends it to the web browser, allowing it to connect to the website.
DNS Records
- A records - An A record maps a domain name to the IP address (Version 4) of the computer hosting the domain. An A record uses a domain name to find the IP address of a computer connected to the internet.
- AAAA records - DNS AAAA records match a domain name to an IPv6 address. DNS AAAA records are exactly like DNS A records, except that they store a domain’s IPv6 address instead of its IPv4 address.
- CNAME - The ‘canonical name’ (CNAME) record is used in lieu of an A record, when a domain or subdomain is an alias of another domain. All CNAME records must point to a domain, never to an IP address.
- MX - A DNS ‘mail exchange’ (MX) record directs email to a mail server. The MX record indicates how email messages should be routed in accordance with the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP, the standard protocol for all email). Like CNAME records, an MX record must always point to another domain.
- TXT - The DNS ‘text’ (TXT) record lets a domain administrator enter text into the Domain Name System (DNS).
- NS - The DNS ‘name server’ (NS) record is used to point a domain or subdomain to a DNS server. The NS record is used to delegate a DNS zone to use a specific DNS server.
- SOA - The DNS ‘start of authority’ (SOA) record is used to identify the authoritative name server for a DNS zone, and to specify administrative contact information for the zone.
- SRV - The DNS ‘service’ (SRV) record is used to specify the location of services (for example, mail servers) and the protocols they support.
- PTR - The DNS ‘pointer’ (PTR) record is used to map an IP address to a domain name. PTR records are used in reverse DNS lookups.
- SPF - The DNS ‘sender policy framework’ (SPF) record is used to prevent email spoofing. SPF records are used to identify which mail servers are authorized to send email for a domain.
- DKIM - The DNS ‘domain keys identified mail’ (DKIM) record is used to prevent email spoofing. DKIM records are used to verify that an email message was sent by a legitimate sender.
- DMARC - The DNS ‘domain-based message authentication, reporting and conformance’ (DMARC) record is used to prevent email spoofing. DMARC records are used to verify that an email message was sent by a legitimate sender.
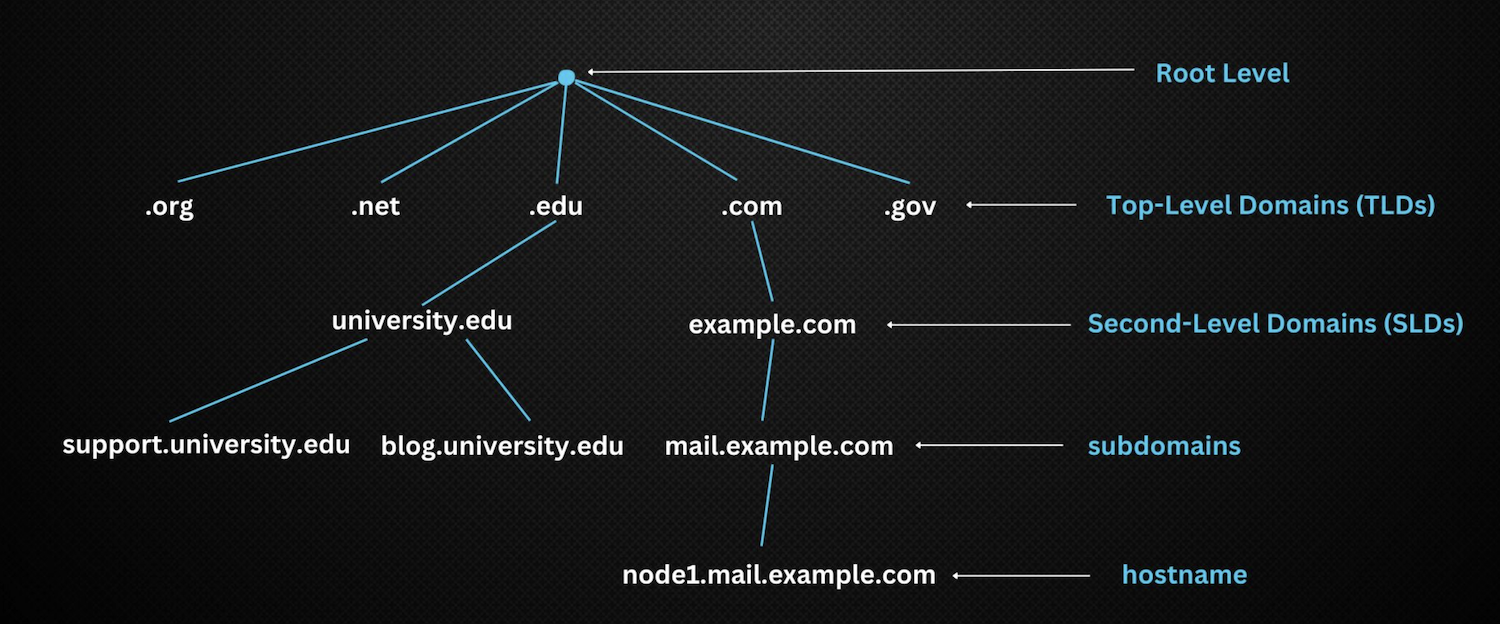
DNS Hierarchy
Defining DNS Zones
DNS Zones play a crucial role in managing various segments of the DNS namespace. In simple terms, a DNS zone is a part of the domain name space that a specific entity or organization administers. It’s a repository of DNS settings and records for a domain, enabling administrators to effectively manage the components of domains within their control.
Primary vs. Secondary DNS
Knowing the distinction between primary (master) and secondary (slave) DNS servers is vital to preserving a robust DNS infrastructure. The primary DNS server is an authoritative source of information for a specific zone, safeguarding the master copy of data in its zone file. Conversely, the secondary DNS server possesses a copy of the zone file from the primary DNS server, acting as a backup to ensure DNS continuity and availability.
Exploring DNS Root Servers
DNS root servers are a fundamental part of the DNS hierarchy, supporting the resolution of domain names. These servers initiate the process of resolving (translating) human-readable domain names into IP addresses. There are 13 sets of root servers worldwide, managed by 12 independent organizations, to ensure the internet operates reliably and stably.
Understanding Reverse DNS (rDNS)
Reverse DNS (rDNS) is a DNS function that maps IP addresses back to domain names. It’s the inverse operation of the DNS, primarily used for logging and troubleshooting. For instance, mail servers often utilize rDNS to verify the domain name of incoming connections, providing an extra layer of security against spam emails.
Importance of Accurate DNS Zone Files
Maintaining accurate and current DNS zone files is critical for efficient DNS resolution. These files contain the specifics of every domain within the zone, including their corresponding IP addresses. Any inaccuracies or outdated information can lead to DNS resolution errors, impacting the availability of websites and services. Regularly updating and verifying the accuracy of DNS zone files is a crucial practice for any organization.
DNS Lookups: Recursive and Iterative
Two distinct types of DNS lookups exist: recursive and iterative. Each plays a specific role in the DNS lookup process, contributing to the seamless navigation we enjoy online.
When a client requests a DNS lookup, it can be handled in two ways: recursively or iteratively. In a recursive lookup, the DNS resolver, often managed by your Internet Service Provider (ISP), takes full responsibility for the query. It will contact various DNS servers until it finds the authoritative server with the requested IP address. The resolver then returns this information to the client.
On the other hand, an iterative lookup works differently. The DNS resolver provides the client with the best answer it can based on its cache. If it doesn’t have the answer, it guides the client to a DNS server that might. The client then must request the information from this new server, continuing the process until it finds the answer.
DNS Security
DNS is vulnerable to several security threats, including DNS spoofing, DNS cache poisoning, and DNS tunneling. DNS spoofing involves redirecting traffic to a fake website by changing the DNS mapping. DNS cache poisoning involves corrupting the DNS cache to redirect traffic to a fake website. DNS tunneling involves using DNS traffic to bypass firewalls and send data outside the network.
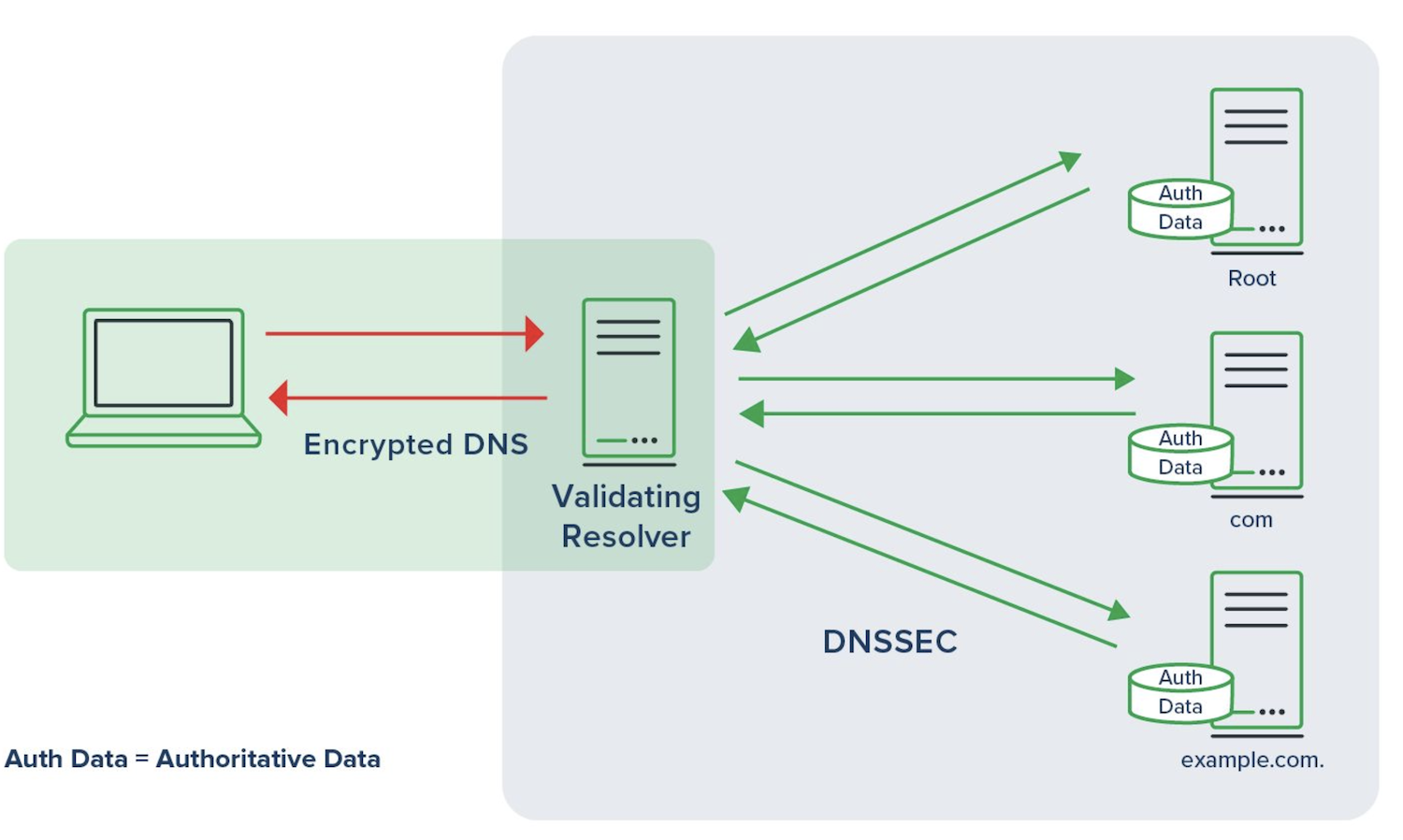
To prevent these security threats, DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions) is used. DNSSEC adds digital signatures to DNS records to ensure that they are authentic and have not been tampered with.
Common DNS Security Threats
Several threats lurk in the shadows of the DNS, the most common ones being DNS spoofing, DNS amplification attacks, and DNS hijacking. DNS spoofing, or cache poisoning, involves corrupting the cache data of a DNS resolver to redirect queries to a malicious site. On the other hand, DNS amplification attacks include cybercriminals exploiting publicly accessible DNS servers to launch a massive DDoS attack on a target. Lastly, DNS hijacking redirects the traffic from a website to a different one without the user’s knowledge. Awareness of these threats is the first step towards safeguarding your DNS infrastructure.
DNSSEC and Its Role in DNS Security
One of the most effective methods of ensuring DNS security is using DNSSEC or Domain Name System Security Extensions. DNSSEC provides a layer of authentication and integrity to the DNS. It employs digital signatures based on public-key cryptography to validate the authenticity of DNS data, thereby preventing unauthorized modifications.
DNS Over TLS (DoT)
The design principle for DNS over TLS (DoT) is simple: Make no changes to the DNS message format, just move everything from UDP port 53 to TCP port 853 and add TLS encryption on top of it. Deploying DoT requires significant coordination and planning, mainly due to the need for using a new TCP port. In addition to having a DoT client and a DoT server, all network devices along the path must open TCP port 853. However, DoT offers advantages for administrators as it is easier to control and block, making it better suited for on-premises private networks.
With DoT, administrators can configure clients to automatically switch to DoT when available (called opportunistic encryption). This means DoT clients can be configured to fall back to Do53 if there is no suitable DoT server. Alternatively, the client can have a strict profile where it must send DNS communications only over DoT. If no DoT servers are available, the client will not perform any DNS resolution.
DNS Over HTTPS (DoH)
The design goal for DNS over HTTPS (DoH) from the start was to make DoH messages indistinguishable from other HTTPS messages. Using DoH is simple for most users because many web browsers and some operating systems already support it. Users can easily enable DoH on the client, point to any public DoH server on the Internet, and start using it because most networks permit outbound traffic on port 443 by default (the same port as HTTPS).
While enabling DoH is easy, routing DNS traffic in this way poses significant problems for security practitioners. The main challenge is that DoH messages cannot be distinguished from other HTTPS traffic. In other words, when using DoH, DNS-specific threat activity cannot be detected, controlled, or blocked. In fact, this is one of the reasons why red teaming tools, such as ColbaltStrike and Silver, make extensive use of DoH.
Domain Registration
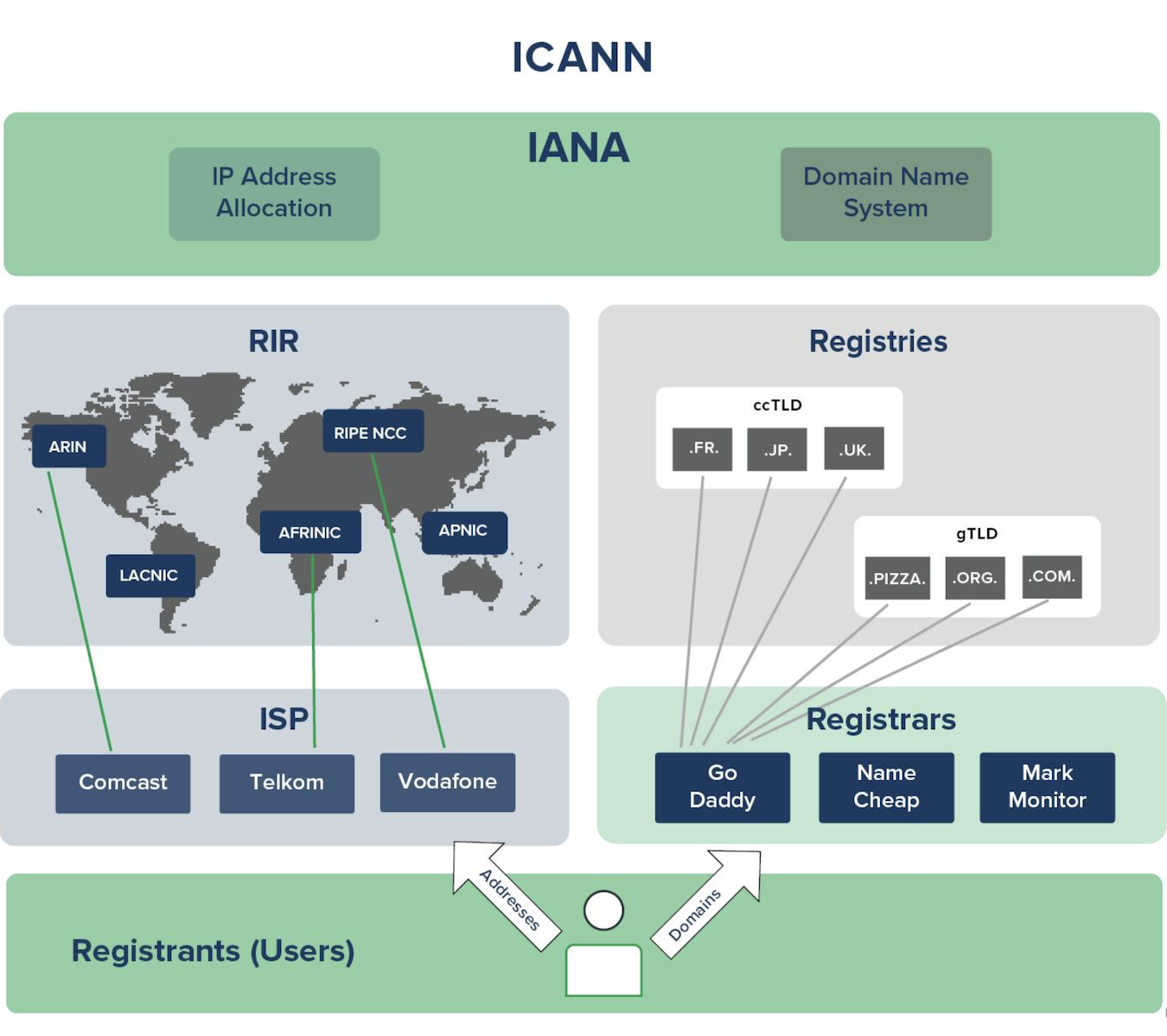
Conclusion
DNS is a crucial component of the internet, and understanding its basics is essential for anyone working in the field of IT. In this 30 minutes guide, we have discussed how DNS works, DNS records, and DNS security. By following the best practices for DNS security, we can ensure the integrity and confidentiality of DNS data and prevent security threats.
Reference
https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/dns/dns-recordsJoshua M Kuo, Ross Gibson J.D., The Hidden Potential of DNS In Security: Combating Malware, Data Exfiltration, and more - The Guide for Security Professionals, 2023https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc7858https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc8484https://outflank.nl/blog/2018/10/25/building-resilient-c2-infrastructues-using-dns-over-https/https://ipsnews.net/business/2024/03/23/mastering-the-internets-address-book-an-in-depth-guide-to-understanding-the-domain-name-system-dns/