Introduction to Cloud Service Design Pattern
Nowadays, design patterns are useful for building reliable, scalable, and secure applications in cloud, mobile, backend, and frontend environments.

What is a Design Pattern
Cloud applications have unique characteristics, such as unpredictable workloads, commodity hardware, and services provided to untrusted users. These factors create a range of problems when building and designing applications for the cloud, such as configuration, authentication, and authorization.
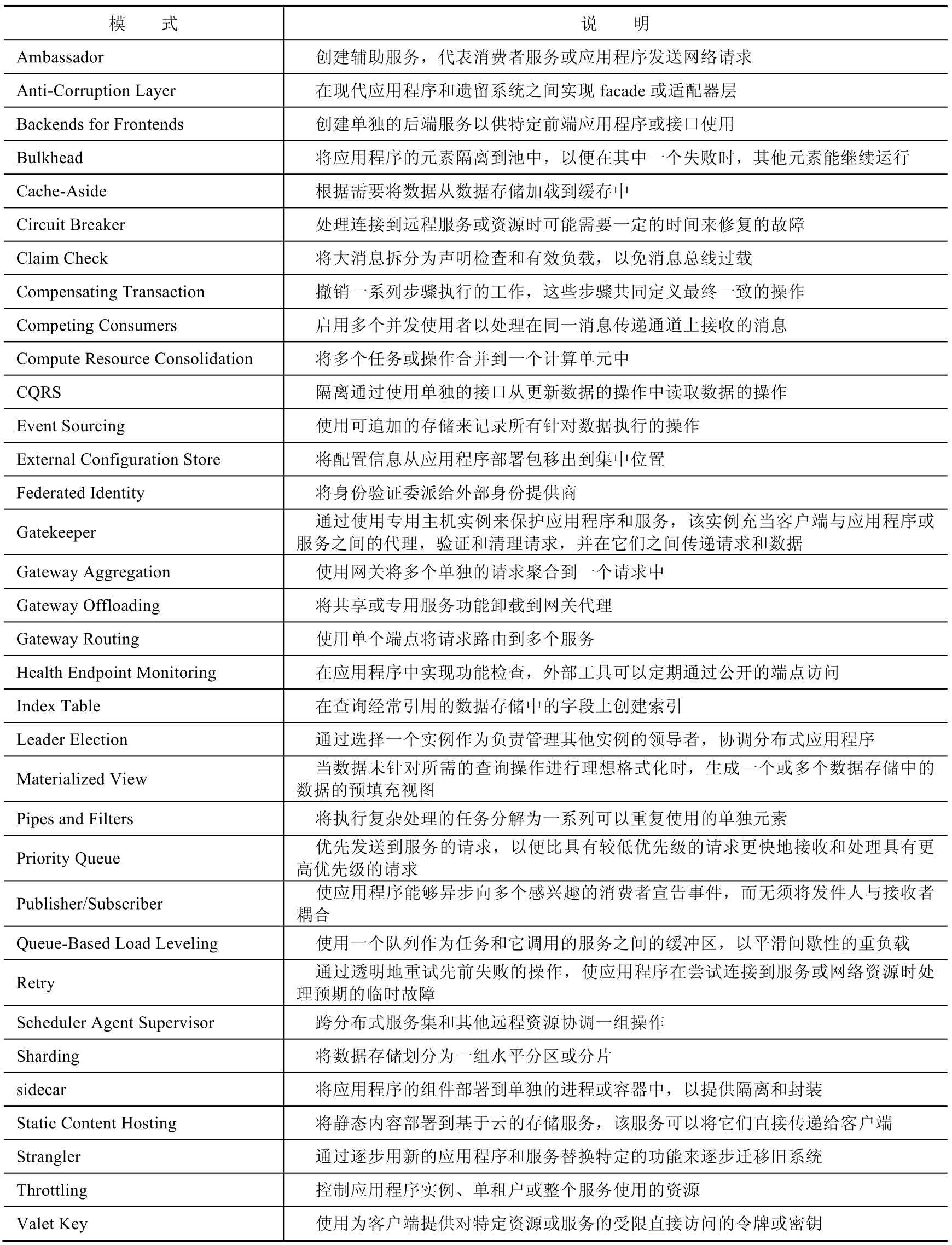
Design patterns are best-practice solutions for common software design problems. They provide a template for solving problems that you may not even know you have.
A design pattern is a reusable solution for addressing common software design problems. It is not a finished design that can be directly transformed into code; rather, it is a template or guideline for solving a problem that can be used in many different situations.
Cloud design patterns are useful for building reliable, scalable, and secure applications in the cloud. Each Azure pattern discusses design considerations and contains code samples or snippets to explain how it can be implemented on Microsoft Azure. Most of the design patterns can be used for any distributed system, whether hosted on Azure or another cloud platform.
Introduction
In recent years, cloud computing has become increasingly popular due to its scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. However, designing and deploying cloud services can be complicated and challenging. To overcome these challenges, developers can use cloud service design patterns. Cloud service design patterns are proven solutions to common cloud computing challenges that can help developers design and implement cloud services more efficiently and effectively. In this blog post, we will discuss three common cloud service design patterns.
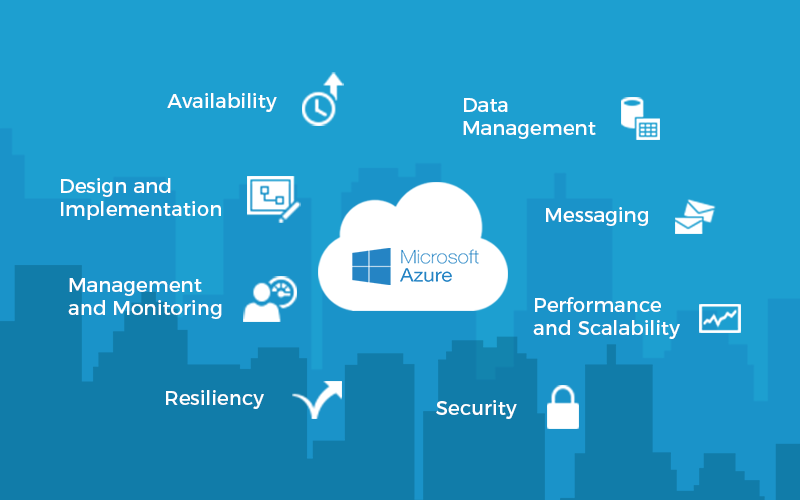
What are the challenges in cloud development?
1. Availability
Availability is the proportion of time that the system is functional and working, usually measured as a percentage of uptime. It can be affected by system errors, infrastructure problems, malicious attacks, and system load. Cloud applications typically provide users with a service level agreement (SLA), so applications must be designed to maximize availability.
2. Design and Implementation
Good design encompasses factors such as consistency and coherence in component design and deployment, maintainability to simplify administration and development, and reusability to allow components and subsystems to be used in other applications and scenarios.
Decisions made during the design and implementation phase have a huge impact on the quality and total cost of ownership of cloud-hosted applications and services.
3. Performance & Scalability
Performance is an indication of the system’s responsiveness to execute any action within a given time interval, while scalability is the ability of a system to handle increases in load without impacting performance or to readily increase available resources.
Cloud applications typically encounter variable workloads and peaks in activity. Instead, applications should be able to scale out within limits to meet peaks in demand and scale in when demand decreases. Scalability concerns not just compute instances, but other elements such as data storage and messaging infrastructure.
4. Management and Monitoring
Cloud applications run in a remote datacenter where you may not have full control of the infrastructure or operating system. This can make management and monitoring more difficult than an on-premises deployment.
Applications must expose runtime information that administrators and operators can use to manage and monitor the system, as well as support changing business requirements and customization without requiring the application to be stopped or redeployed.
5. Data Management
Data management is a key element of cloud applications and influences most quality attributes. Data is typically hosted in different locations and across multiple servers for reasons such as performance, scalability, or availability, and this can present a range of challenges. For example, data consistency must be maintained, and data will typically need to be synchronized across different locations.
6. Security
Security is the capability of a system to prevent malicious or accidental actions outside of the designed usage and to prevent disclosure or loss of information. Cloud applications are exposed on the Internet outside trusted on-premises boundaries, are often open to the public, and may serve untrusted users. Applications must be designed and deployed in a way that protects them from malicious attacks, restricts access to only approved users, and protects sensitive data.
7. Messaging
The distributed nature of cloud applications requires a messaging infrastructure that connects the components and services, ideally in a loosely coupled manner in order to maximize scalability. Asynchronous messaging is widely used and provides many benefits, but also brings challenges such as the ordering of messages, poison message management, idempotency, and more.
8. Resiliency
Resiliency is the ability of a system to gracefully handle and recover from failures. The nature of cloud hosting, where applications are often multi-tenant, use shared platform services, compete for resources and bandwidth, communicate over the Internet, and run on commodity hardware, means there is an increased likelihood that both transient and more permanent faults will arise. Detecting failures and recovering quickly and efficiently is necessary to maintain resiliency.
Conclusion
Cloud service design patterns provide developers with a set of proven solutions to common cloud computing challenges. By using these patterns, developers can design and deploy cloud services more efficiently and effectively, reducing costs, improving performance, and increasing scalability. In this blog post, we discussed three common cloud service design patterns: Microservices, Serverless Computing, and Auto Scaling. Developers can use these patterns to build robust, scalable, and cost-effective cloud services.
Reference
https://www.ijert.org/research/introduction-to-cloud-design-patterns-IJERTV9IS080171.pdfhttps://medium.com/@maheshsonaiya/cloud-design-patterns-cac98e878698https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/patterns/