What is Load Balance
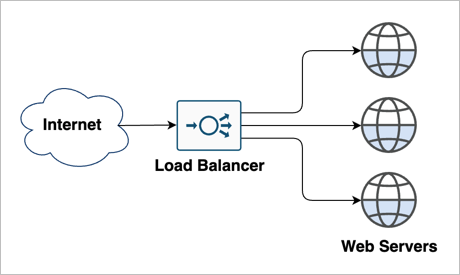
Introduction
Load balancing is a crucial concept in modern IT infrastructure. It ensures that a server or network does not get overwhelmed by an influx of traffic, improving the overall performance and reliability. In this guide, we will cover the basics of load balancing in just 30 minutes. You’ll learn what load balancing is, how it works, and the different types of load balancing.
Reading List
What is Load Balancing?
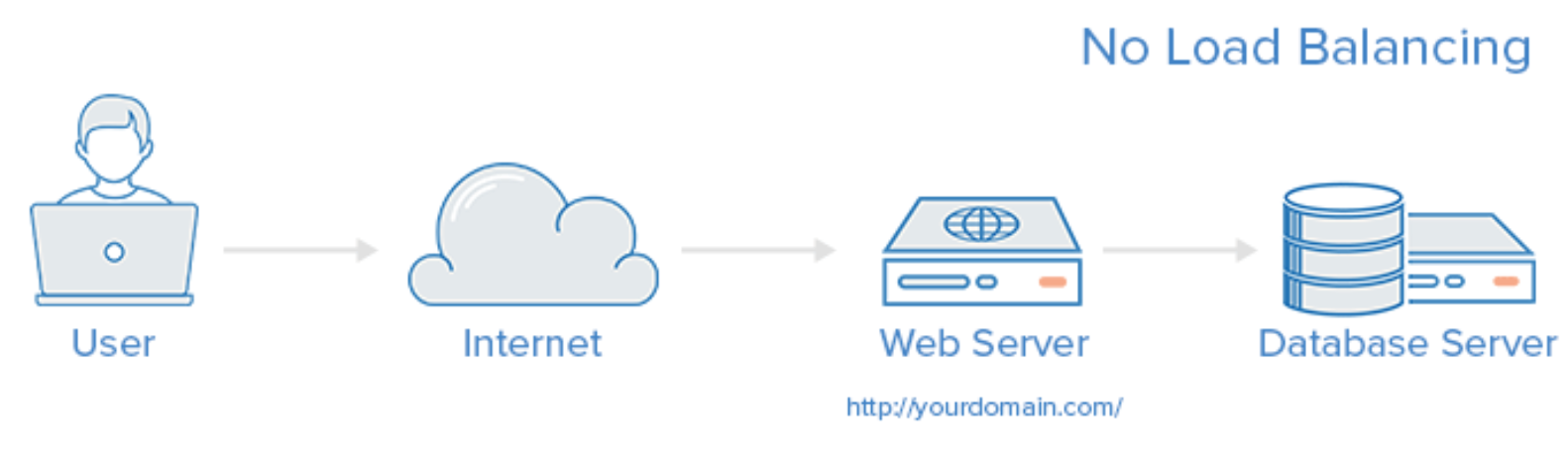
Load balancing is the process of distributing traffic across multiple servers, networks, or resources. It is used to prevent any single server or resource from becoming overwhelmed and failing to respond to requests. Load balancing can be performed at various levels, including network, transport, and application layers.
How Load Balancing Works
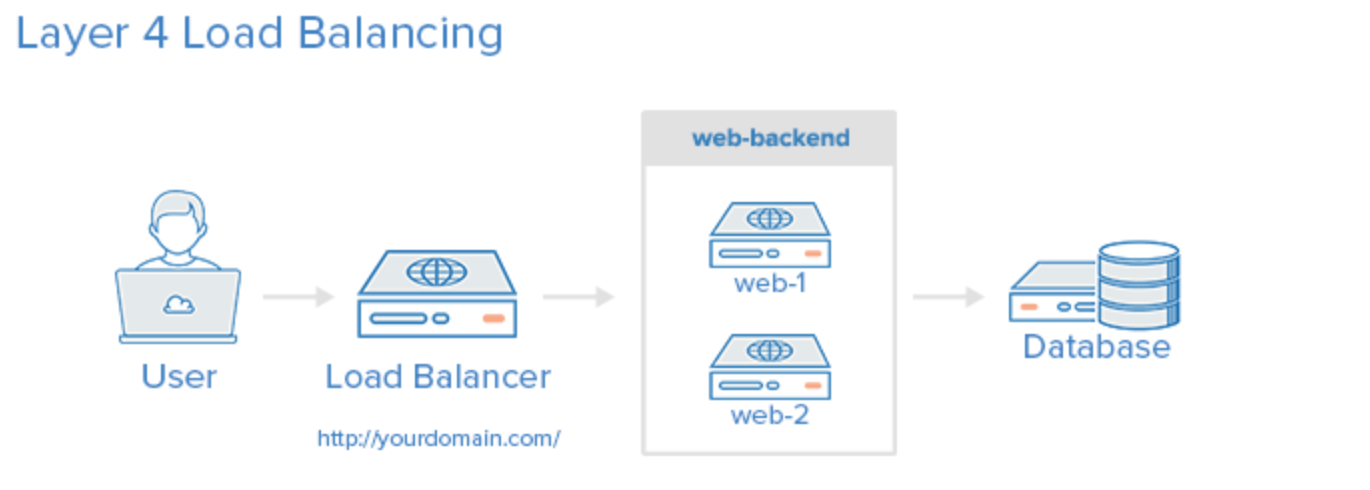
Load balancing works by distributing traffic across multiple servers or resources. There are several ways to implement load balancing, but the most common method is to use a load balancer. A load balancer is a device or software that acts as a traffic cop, directing incoming traffic to the most available server or resource.
Benefits of Load Balancing
There are several benefits to introducing load balancers into your system but not limited to the following:
- Reduced downtime
- Scalability
- Redundancy
- Flexibility
- Efficiency
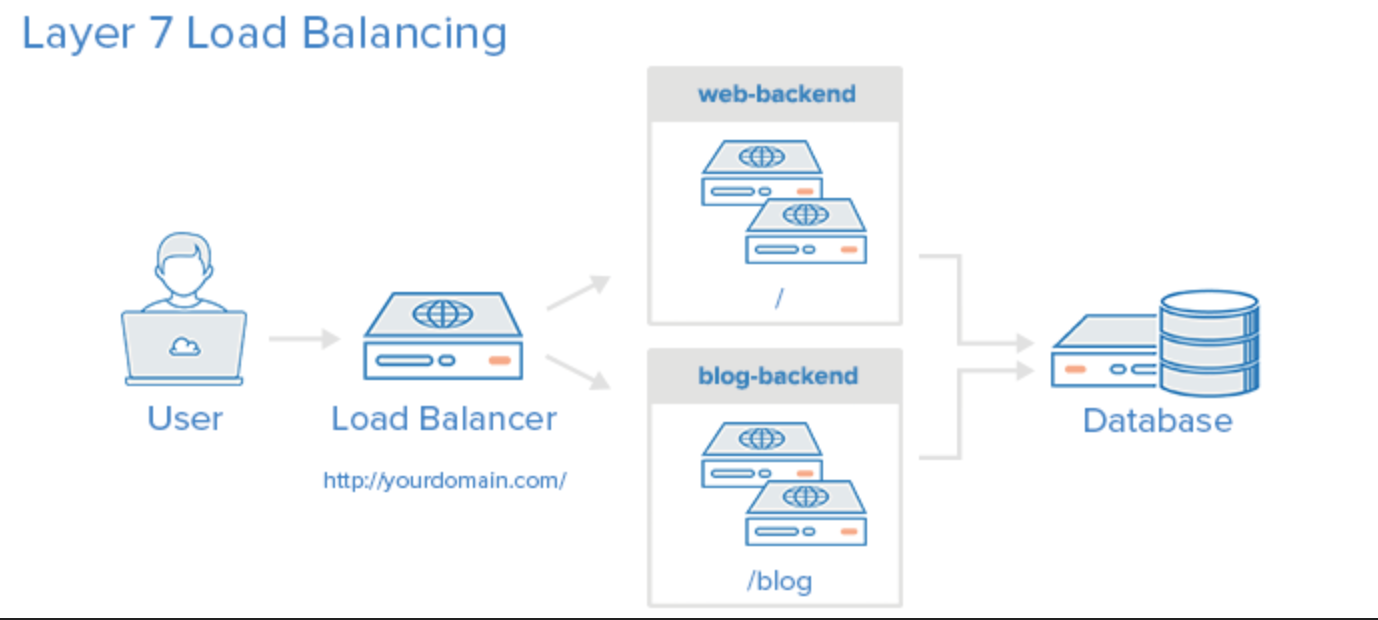
Types of Load Balancing
There are several types of load balancing, including round-robin, least connections, IP hash, and content-based load balancing. Round-robin load balancing distributes traffic in a circular pattern, while least connections load balancing directs traffic to the server with the least number of active connections. IP hash load balancing uses the source IP address of the client to determine which server to send traffic to, while content-based load balancing directs traffic based on the type of content being requested.
- HTTP Load Balancing:
https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/load-balancer/tcp-udp-load-balancer/ - TCP and UDP Load Balancing:
https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/load-balancer/tcp-udp-load-balancer/
Load Balancing Options
- Bamboo: This is a daemon that automatically configures HAProxy instances deployed on Apache Mesos and Marathon.
- Envoy: Envoy is a high-performance distributed proxy written in C++. It was originally developed at Lyft. Envoy was designed for use with single services and applications, and to function as a communication bus and data plane for service meshes. It is the default data plane in Istio.
- HAProxy: This stable, mature, and battle-proven workhorse might not be feature-rich, but it’s reliable. It’s often used in conjunction with NGINX. Integrations with virtually anything you can think of are available.
- kube-proxy: This runs on each node of a Kubernetes cluster and updates service IPs. It supports simple TCP/UDP forwarding and round-robin load balancing. Note, however, that kube-proxy is solely for cluster-internal load balancing. It also functions as a service discovery support component.
- MetalLB: MetalLB is a load-balancer implementation designed for bare-metal Kubernetes clusters. It addresses the lack of a default implementation for such clusters in Kubernetes. In other words, you typically need to be in a public cloud environment to benefit from this functionality. However, note that MetalLB may require one or more routers capable of using the BGP protocol to function properly.
- NGINX: NGINX is a leading solution in this space. It offers support for round-robin, least-connected, and IP-hash strategies. Additionally, it provides on-the-fly configuration, monitoring, and many other essential features.
- Traefik: This is the rising star in its category. Emile Vauge, the lead developer of Traefik, is certainly doing something right. I appreciate it as it’s similar to HAProxy but includes a range of backends, like Marathon and Consul, right out of the box.
- Vamp-router: Inspired by Bamboo and Consul–HAProxy, Magnetic.io developed Vamp-router. This router supports configuration updates via a REST API or ZooKeeper. It also includes routing and filtering capabilities for canary releasing and A/B testing, access control lists (ACLs), and the provision of statistics.
- Vulcand: A reverse proxy designed for HTTP API management and microservices, inspired by Hystrix.
Reference
https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/load-balancer/http-load-balancer/https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/performance/what-is-load-balancing/https://architecturenotes.co/load-balancers/https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/load-balancer/load-balancer-overviewhttps://www.f5.com/glossary/load-balancer