Cloud Computing Basics

Introduction
Cloud computing is a term used to describe the delivery of computing services over the internet. It is a technology that has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals store, access, and process data. Cloud computing makes it possible for users to access computing resources on-demand, without the need for physical infrastructure such as servers and storage devices. In this blog post, we will explore the basics of cloud computing and how it works.
Cloud service models
IaaS
IaaS is perhaps the most well-known service model of the cloud. When enterprises initiate migration to cloud providers, they typically start with IaaS. This involves a lift and shift of their (virtual) machines to resources hosted in the cloud. The cloud provider only manages the infrastructure for the customer: network, storage, compute, and the virtualization layer. The latter is important since customers share physical resources in the cloud. These resources, such as servers, are virtualized, so they can host multiple instances.
PaaS
With PaaS, cloud providers take more responsibility for resources, including operating systems and middleware. A good example is a database platform. Customers only need to run a database instance on a database platform; they don’t have to take care of the database platform itself (e.g. MySQL or PostgreSQL), as the cloud provider handles it, including the underlying operating systems.
SaaS
SaaS is generally considered the future model for cloud services. In this model, the cloud provider manages everything in the software stack, from the infrastructure to the actual application with all its components, including data. Software updates, bug fixes, and infrastructure maintenance are all handled by the cloud provider. The user accesses the application through a portal or API without installing software on local machines, typically using a subscription.
FaaS
FaaS refers to a cloud service that enables the development and management of serverless computing applications. Serverless does not mean that there are no services involved, but developers can program services without worrying about setting up and maintaining a server; the cloud provider takes care of that. The big advantage is that the programmed service only uses the exact amount of resources, such as CPU and memory, instead of an entire virtual machine.
CaaS
An increasing number of enterprises are adopting container technology to host, run, and scale their applications. To run containers, developers need to set up a runtime environment for them. Typically, this is done with Kubernetes, which is the industry standard for hosting, orchestrating, and running containers. However, setting up Kubernetes clusters can be complex and time-consuming. The solution is Container as a Service (CaaS), which provides an easy way to set up container clusters.
XaaS
Anything as a Service (XaaS) is a term used to describe the idea that users can have everything as a service. The concept is widely spread across various domains, such as Hardware as a Service (HaaS), Desktop as a Service (DaaS), or Database as a Service (DBaaS). This idea is not limited to IT, though. The general idea is that companies will offer services and products in an as-a-service model, using the cloud as the digital enabler. Examples include food delivery to homes, ordering taxis, or consulting a doctor using apps.
Public Cloud
Public cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the internet to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale. Unlike traditional data centers, public clouds are owned and operated by third-party providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and IBM Cloud, which offer their services to multiple customers on a shared infrastructure.
Advantages of Public Cloud
- Cost-effectiveness: Public clouds offer pay-as-you-go pricing, which enables customers to only pay for the services they consume, without having to invest in expensive hardware and software. This can result in significant cost savings, especially for small and medium-sized businesses.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Public clouds provide on-demand access to computing resources, allowing customers to easily scale up or down based on their changing needs. This makes it easier for businesses to respond to changes in demand and to handle peak traffic loads.
- High Availability and Reliability: Public clouds are designed to provide high availability and reliability, with built-in redundancy and disaster recovery capabilities. This ensures that applications and data remain available and accessible, even in the event of a failure.
- Security: Public clouds employ advanced security measures to protect customer data, such as encryption, identity and access management, and network security.
Disadvantages of Public Cloud
- Dependence on Internet Connectivity: Public clouds rely on internet connectivity to deliver their services, which can impact performance and availability in the event of an outage or disruption.
- Security Concerns: Despite the advanced security measures in place, some customers may still be concerned about the security of their data in a shared environment.
- Lock-in: Some public cloud providers may lock customers into using their services, making it difficult to switch to a different provider.
- Lack of control: Public clouds are managed and operated by third-party providers, which means customers may have limited control over the configuration and management of their resources.
In conclusion, public cloud computing provides businesses with a flexible, cost-effective, and scalable solution for their computing needs. While there are some challenges associated with public clouds, such as dependence on internet connectivity and security concerns, the benefits far outweigh the risks for many organizations. By carefully evaluating their requirements and considering the trade-offs, businesses can determine whether public clouds are the right fit for their needs.
Private Cloud
Private cloud computing is a type of cloud computing that provides dedicated and isolated computing resources over the internet or a private network. Unlike public clouds, which are shared among multiple customers, private clouds are dedicated to a single organization and provide more control, security, and customization. Private clouds can be deployed on-premises, in a data center, or hosted by a third-party provider.
Advantages of Private Cloud
- Security: Private clouds offer a higher level of security and privacy compared to public clouds, as the infrastructure is dedicated to a single organization and is not shared with other customers. This makes it easier to control access to sensitive data and to meet regulatory requirements.
- Customization: Private clouds provide more customization options, allowing organizations to tailor the infrastructure to meet their specific needs and requirements.
- Control: Private clouds provide organizations with more control over their computing resources, including the ability to manage their own security and data privacy policies.
- Performance: Private clouds can offer better performance compared to public clouds, as the resources are dedicated to a single organization and not shared with other customers.
Disadvantages of Private Cloud
- Cost: Private clouds can be more expensive compared to public clouds, as the infrastructure is dedicated to a single organization and requires a higher level of investment in hardware and software.
- Complexity: Private clouds can be more complex to manage and maintain compared to public clouds, as organizations are responsible for the configuration and management of the infrastructure.
- Scalability: Private clouds may not offer the same level of scalability as public clouds, as organizations may need to invest in additional hardware and software to accommodate growth.
In conclusion, private cloud computing provides organizations with dedicated and isolated computing resources, offering a higher level of security, customization, and control. While private clouds can be more expensive and complex compared to public clouds, they are an ideal solution for organizations with strict security and privacy requirements. By carefully evaluating their requirements and considering the trade-offs, organizations can determine whether a private cloud is the right fit for their needs.
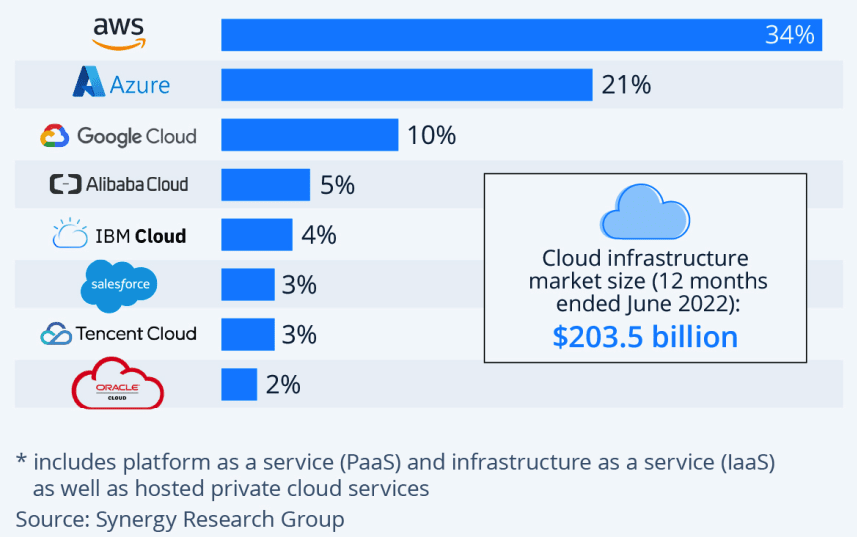
Multi Cloud
Multi-cloud refers to the use of two or more cloud computing systems simultaneously. The deployment might use public clouds, private clouds, or some combination of the two. Multi-cloud deployments aim to offer redundancy in case of hardware or software failures and to avoid vendor lock-in.
Business requirements for multi-cloud
- Interoperability
- Configurability
- Performance
- Discoverability
- Robustness
- Portability
- Usability
Reference
- Jeroen Mulder - Multi-Cloud Strategy for Cloud Architects Learn how to adopt and manage public clouds by leveraging BaseOps, FinOps, and DevSecOps, 2nd Edition (2023)
https://www.techopedia.com/definition/33511/multi-cloud-strategyhttps://www.opengroup.org/togaf