NoSQL
Introduction
In the ever-evolving world of technology, data has become the backbone of numerous industries. As the volume and complexity of data continue to grow exponentially, traditional relational databases have started to show limitations in terms of scalability and flexibility. This has paved the way for the emergence of NoSQL databases, offering a new approach to data storage and retrieval. In this blog post, we will explore the rise of NoSQL databases, their advantages, and their impact on the industry.
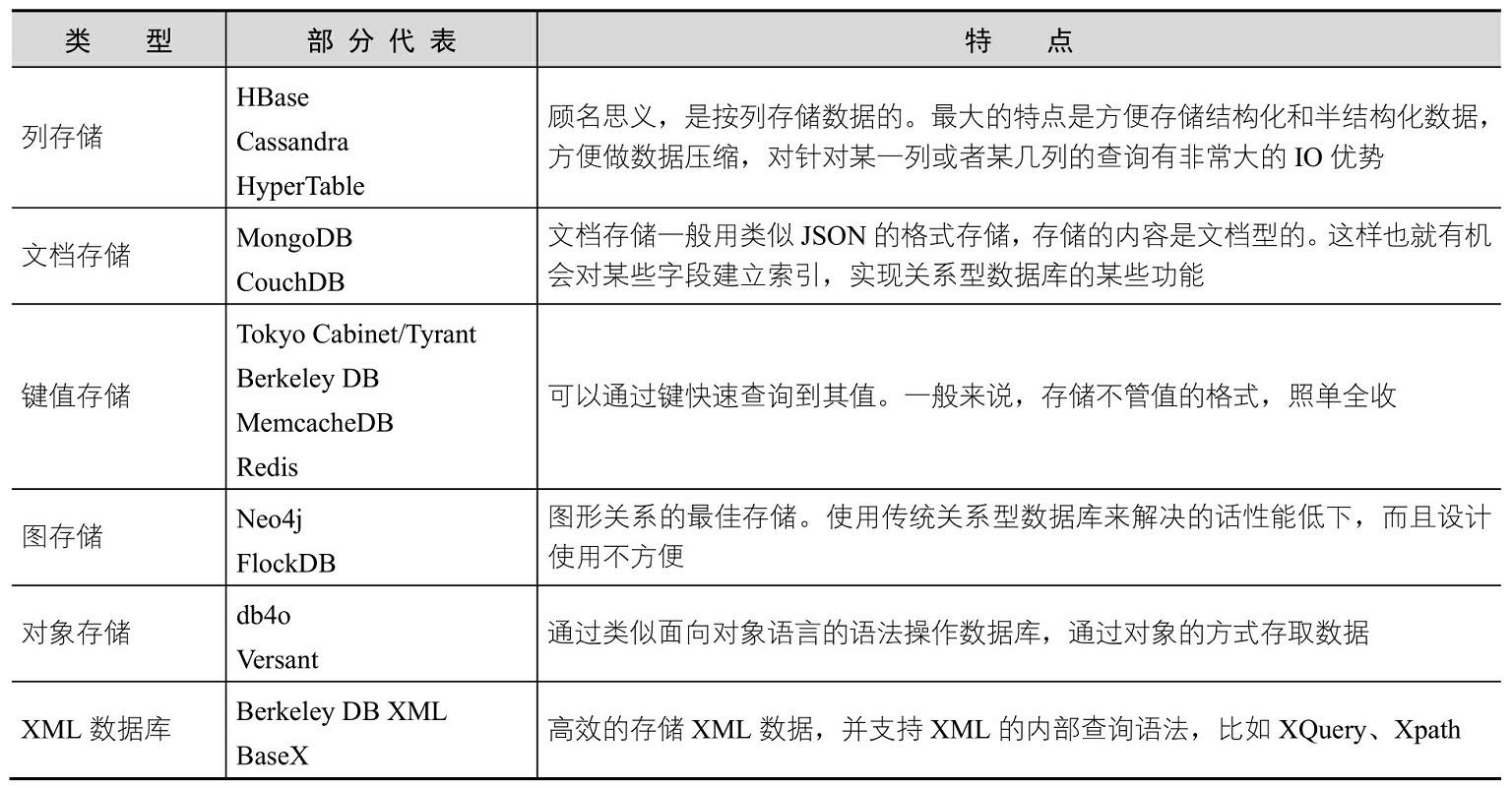
key-value databases
- Riak
- Redis
- Memcached DB
- Berkeley DB
- HamsterDB
- Amazon DynamoDB
- Project Voldemort (an open-source implementation of Amazon DynamoDB)
document databases
- MongoDB
- CouchDB
- Terrastore
- OrientDB
- RavenDB
column-family stores
- Cassandra
- HBase
- Hypertable
- Amazon SimpleDB
graph databases
- Neo4J
- Infinite Graph
- OrientDB
- FlockDB
Conclusion
NoSQL databases have revolutionized the way we handle and manage data. Their scalability, flexibility, and performance have made them a popular choice for modern applications. As technology continues to advance and data continues to grow, NoSQL will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the future of data storage and retrieval. Whether it’s handling massive amounts of data or adapting to rapidly changing requirements, NoSQL databases provide a powerful solution that breaks the mold of traditional relational databases.
Reference
- NoSQL Distilled - A Brief Guide to the Emerging World of Polyglot Persistence (Pramod J. Sadalage, Martin Fowler)
https://medium.com/must-know-computer-science/system-design-caching-acbd1b02ca01https://www.integrate.io/blog/the-sql-vs-nosql-difference/