Ansible

Introduction
In the world of IT, managing servers and applications can be a daunting task, especially when there are multiple servers and applications to manage. This is where Ansible comes in handy. Ansible is an open-source automation tool that enables IT professionals to manage and automate IT infrastructure. Ansible is easy to learn, easy to use, and is quickly becoming a popular choice for IT automation.
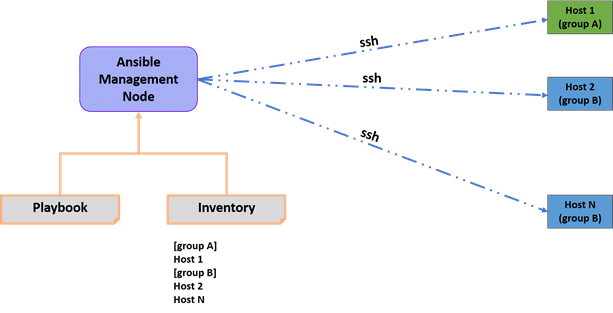
Ansible Architecture

Project example
.
├── group_vars
│ ├── all
│ │ ├── vars.yml
│ │ └── secrets.yml
│ ├── db
│ │ └── vars.yml
│ └── web
│ └── vars.yml
├── host_vars
│ ├── mysqlserver.yml
│ ├── pgserver.yml
│ ├── node1.example.com
│ └── node2.example.com
├── playbook.yml
└── inventory
└── ansible.cfg

1. Control Node
At the heart of Ansible’s architecture is the control node, a machine where Ansible is installed and runs. From this node, administrators and automation engineers execute Ansible playbooks, which are scripts written in YAML that describe the automation tasks to be performed. No agents need to be installed on the remote hosts, making Ansible highly scalable and reducing network overhead.
2. Managed Nodes
Managed nodes are the servers, systems, or devices managed and automated using Ansible. These nodes are accessed by the control node over SSH (for Linux/Unix systems) or WinRM (for Windows systems). Ansible does not require any agents to be installed on the managed nodes, leveraging existing security and authentication frameworks for communication and execution.
3. Inventory
The inventory is a list of managed nodes that Ansible can automate. It can be defined in a simple text file or dynamically generated from external sources. The inventory specifies how to reach the nodes and may classify them into groups for easier management and targeting in playbooks.
[web_servers]
app1_host ansible_host=app1.example.com
app2_host ansible_host=app2.example.com
[group_name:children]
group1
group2
[group1]
www[01:50].example.com
server[01:20].example.com
192.168.[100:105].[0:255]
[a:c].node.example.com
[group2]
node1 http_port=82 maxRequestsPerChild=202
node2 http_port=92 maxRequestsPerChild=303
[webservers]
www[01:30:2].example.com
4. Modules
Modules are units of code that Ansible executes on managed nodes. There are hundreds of modules available in Ansible for a wide range of tasks, from managing files and services to working with cloud platforms and APIs. Modules can be executed directly from the command line or through playbooks.
ansible-galaxy collection install amazon.aws
e.g.
ec2_vpc_subnet: This module is used to create, modify, and delete VPC subnets in Amazon Web Services. It allows you to specify the subnet’s CIDR block, availability zone, VPC ID, and other optional attributes, such as tags and route table association.ec2_vpc_igw: This module is used to create, modify, and delete internet gateways in Amazon VPC. An internet gateway is a horizontally scaled, redundant, and highly available VPC component that allows communication between instances in your VPC and the internet. This module allows you to associate the internet gateway with a VPC and add tags to it.ec2_vpc_route_table: This module is used to create, modify, and delete VPC route tables in Amazon Web Services. A route table is a set of rules that determine where network traffic is directed within a VPC. This module allows you to specify the VPC ID, associate the route table with one or more subnets, and add or remove routes from the route table.
Index of all Modules: https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/collections/index_module.html
5. Playbooks
Playbooks are the cornerstone of Ansible’s automation capabilities. Written in YAML, they are easy to read, write, and share. Playbooks describe the desired states of your systems, the tasks to achieve those states, and the order in which those tasks should be executed. They can include variables, templates, and control structures, making them powerful tools for complex automation scripts.
---
- name: "A simple playbook"
hosts: ansible_hosts
gather_facts: true
become: true
become_method: "ansible.builtin.sudo"
tasks:
- name: "Output some information on our host"
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "I am connecting to {{ ansible_nodename }} which is running {{ ansible_distribution }} {{ ansible_distribution_version }}"
- name: Check if docker exists
command: docker --version
register: docker
- name: Check if port 80 is open
wait_for:
port: 80
state: started
timeout: 5
msg: "Nginx not start"
when: docker.stderr == ""
ansible-playbook foo.yml --check
ansible-playbook -i hosts playbook.yml
ansible-playbook foo.yml --check --diff --limit foo.example.com
ansible-lint set-firewall.yml
6. Plugins
Plugins augment Ansible’s core functionality, allowing users to add custom features or integrate with other software and APIs. There are several types of plugins, including connection plugins to handle communication with managed nodes, lookup plugins to retrieve data from external sources, and filter plugins to manipulate data within playbooks.
7. APIs and Extensibility
Ansible’s architecture is designed for extensibility. The tool can be easily integrated with other applications and systems through its APIs. Custom modules and plugins can be developed to extend its capabilities further, making Ansible adaptable to almost any automation scenario.
Ansible for Configuration Management
One of the primary applications of Ansible is configuration management. Ansible makes it easy to configure servers and applications by using a simple, yet powerful, language for defining configuration files. This language is known as YAML, and it is used to define configuration files called playbooks. Playbooks are a set of instructions that Ansible uses to configure servers and applications. The beauty of Ansible is that it can configure multiple servers at once, which saves time and effort.
Generate an ansible.cfg file with all default configurations disabled
ansible-config init --disabled > ansible.cfg
Generate an ansible.cfg file with all default configurations disabled, including all possible configuration options
ansible-config init --disabled -t all > ansible.cfg
e.g. ansible.cfg
[defaults]
inventory=./inventory
remote_user=rhce
ask_pass=false
host_key_checking=false
[privilege_escalation]
become=true
become_method=sudo
become_user=root
become_ask_pass=false
Ansible for Provisioning
Another application of Ansible is provisioning. Provisioning is the process of creating new servers or virtual machines. Ansible can automate this process by using a tool called Vagrant. Vagrant is a tool that allows IT professionals to create and manage virtual machines. Ansible can be used with Vagrant to automate the process of creating new virtual machines. This saves time and effort by eliminating the need to manually create virtual machines.
Ansible for Deployment
The third application of Ansible is deployment. Deployment is the process of moving code from development to production. Ansible can automate this process by using a tool called Jenkins. Jenkins is a tool that allows IT professionals to build, test, and deploy code. Ansible can be used with Jenkins to automate the process of deploying code. This saves time and effort by eliminating the need to manually deploy code.
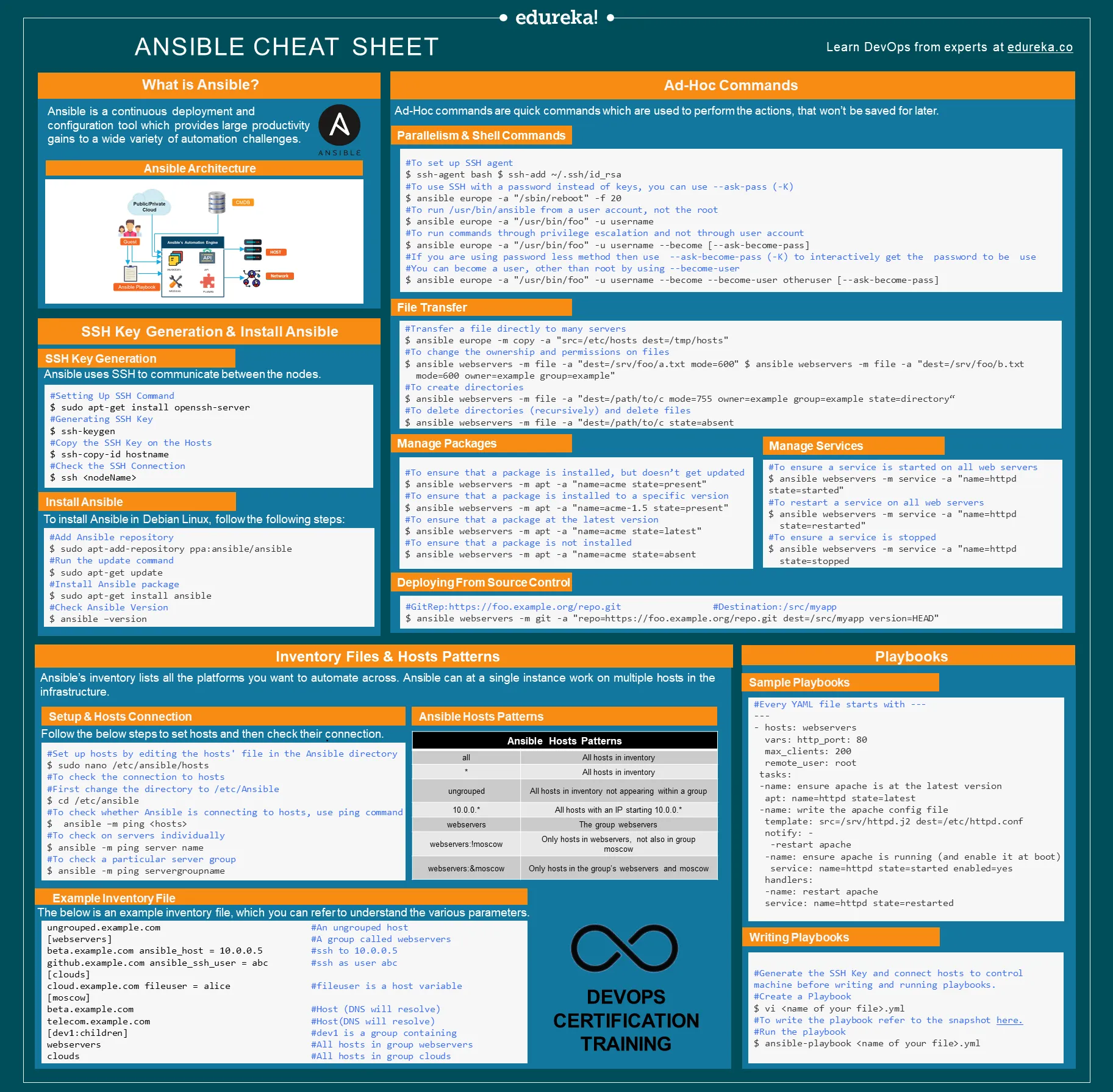
Ansible Cheat Sheet
Ansible Best Practices
Ansible Collection
Collections are a distribution format for Ansible content that can include playbooks, roles, modules, and plugins. You can install and use collections through a distribution server, such as Ansible Galaxy, or a Pulp 3 Galaxy server.
e.g.
## install a collection
ansible-galaxy collection install amazon.aws
- name: Reference a collection content using its FQCN
hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Call a module using FQCN
my_namespace.my_collection.my_module:
option1: value
https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/collections_guide/index.html
Ansible - AWX
AWX provides a web-based graphical interface, management solution, REST API, and task engine built on top of Ansible. This is particularly useful for advanced Ansible use cases. It is one of the upstream projects for the Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform.
Additionally, it adds a lot of functionality to your automation, including credential management, inventory synchronization, and workflow abstraction. It can be a bit overwhelming at first, so let’s see how it works and how you can get started.
Ansible Tower

Other Tools & Platforms
- Chef
- Puppet
- Red Hat Ansible
- Salt
- CFEngine
- Puppet(Ruby)
- fabric(Python)
- pssh/pscp(Python)
- Cpanel
- Plesk
- Nagios
Ansible Usage

ansible [pattern] -m [module] -a "[module options]"
ansible <host-pattern> [-m module_name] [-a args]
[-h] [--version] [-v] [-b] [--become-method BECOME_METHOD] [--become-user
BECOME_USER] [-K | --become-password-file BECOME_PASSWORD_FILE][-i INVENTORY]
[--list-hosts] [-l SUBSET] [-P POLL_INTERVAL] [-B SECONDS] [-o] [-t TREE] [--private-key
PRIVATE_KEY_FILE] [-u REMOTE_USER] [-c CONNECTION] [-T TIMEOUT] [-k |
--connection-password-file CONNECTION_PASSWORD_FILE] [-C] [--syntax-check] [-D] [-e
EXTRA_VARS] [--vault-id VAULT_IDS] [--ask-vault-password | --vault-password-file
VAULT_PASSWORD_FILES] [-f FORKS] [-M MODULE_PATH] [--playbook-dir BASEDIR]
[--task-timeout TASK_TIMEOUT] [-a MODULE_ARGS] [-m MODULE_NAME]
e.g.
ansible all --list-hosts
ansible all -i /home/rhce/ansible/inventory --list-hosts
ansible ungrouped -i inventory --list-hosts
ansible web_server,database_server,kubernetes -i inventory --list-hosts
ansible-inventory --list
ansible all -m ping
ansible group001 -i hosts.ip -m shell -a "run some shell command" --become -f 1 -v
ansible -i hosts.txt group002 -m copy -a "src=fileA dest=/tmp/ mode=0755"
ansible -i hosts.txt group003 -m shell -a "/tmp/fileB.sh"
ansible all -m uri -a "url=https://www.example.com method=GET return_content=yes status_code=200"
ansible webservers -m yum -a "name=httpd state=present"
ansible webservers -m file -a "path=/path/to/test/doc mode=755 owner=rhce group=rhce state=directory"
ansible-playbook -i /path/to/my_inventory_file -u my_connection_user -k -f 3 -T 30 -t my_tag -m /path/to/my_modules -b -K my_playbook.yml
ansible-lint set-firewall.yml
ansible-doc [options] module_name
ansible-doc yum
ansible-doc -l
ansible-doc -j file
Ansible Inventory
[demo:children]
nginx
mysql
[nginx]
192.168.100.101 ansible_ssh_user=ubuntu ansible_ssh_port=22 ansible_python_interpreter=/usr/bin/python3
[mysql]
192.168.100.102 ansible_ssh_user=ubuntu ansible_ssh_port=22 ansible_python_interpreter=/usr/bin/python3
ansible.cfg
[defaults]
private_key_file = ~/.ssh/id_rsa
host_key_checking = False
forks = 300
timeout = 40
deprecation_warnings = False
roles_path = ansible/roles
inventory_plugins = ansible/plugins/inventory
allow_world_readable_tmpfiles=true
[ssh_connection]
ssh_args = -o ForwardAgent=yes -o ControlMaster=auto -o ControlPersist=600s -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no
retries = 5
pipelining = True
control_path = /tmp/ansible-ssh-%%h-%%p-%%r
Playbook Example
---
- name: Provision Apache HTTPD
hosts: web
become: yes
tasks:
- name: Install httpd package
yum:
name: httpd
state: present
- name: Copy index.html to remote node path
copy:
src: index.html
dest: /var/www/html/index.html
- name: Ensure httpd is started
service:
name: httpd
state: started
enabled: true
- name: Open firewall for http
firewalld:
service: http
state: enabled
immediate: yes
permanent: true
ansible-playbook httpd.yml --syntax-check
ansible-playbook httpd.yml
Reference
- Linux自动化运维, 杨寅冬
- Learn Ansible Automate your cloud infrastructure, security configuration, and application deployment with Ansible, Russ McKendrick
- Multi-Cloud Automation with Ansible, Automate, orchestrate, and scale in a multi-cloud world, Sabharwal, Pankaj
- Ansible for Kubernetes by Example: Automate Your Kubernetes Cluster with Ansible, Luca Berton
- Ansible for Kubernetes, Automate app deployment on any scale with Ansible and K8s, Jeff Geerling
https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/index.htmlhttps://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/command_guide/cheatsheet.htmlhttps://dev.to/aws-builders/how-i-use-ansible-to-automate-routine-tasks-by-running-an-adhoc-script-4174https://developers.redhat.com/articles/2024/04/12/event-driven-ansible-rulebook-automationhttps://linuxhandbook.com/ansible-replace-module/https://sleeplessbeastie.eu/2024/03/27/how-to-automate-encryption-and-decryption-of-ansible-vault-using-a-single-password/https://dev.to/shandesai/deep-dive-with-ansible-patching-an-ansible-collection-4e8mhttps://www.dbi-services.com/blog/trigger-a-red-hat-ansible-automation-platform-job-workflow-from-gitlab-ci-cd-pipeline/https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/command_guide/cheatsheet.htmlhttps://www.ansible.com/https://github.com/ansible/awx/blob/devel/tools/docker-compose/README.mdhttps://awxpkg.github.io/rpm/https://developers.redhat.com/articles/2024/07/15/ansible-collection-red-hat-runtimeshttps://github.com/ansible/awxhttps://github.com/ansible/awx-operatorhttps://github.com/kurokobo/awx-on-k3shttps://tecadmin.net/ansible-architecture/https://tecadmin.net/basic-ansible-guide/https://tecadmin.net/setup-kubernetes-cluster-using-ansible/https://medium.com/@souhardyasarkar735/install-and-configure-kubernetes-master-node-using-ansible-playbook-8a098d1bae1bhttps://dev.to/k3n3/ansible-with-task-automation-demo-3k8mhttps://sleeplessbeastie.eu/2024/03/28/how-to-automate-encryption-and-decryption-of-ansible-vault-using-multiple-identities/https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/containers/use-ansible-to-bootstrap-external-container-instances-with-amazon-ecs-anywhere/https://developers.redhat.com/articles/2024/04/12/how-create-automation-mesh-ansible-controller#second_automation_mesh_design_examplehttps://blog.while-true-do.io/ansible-awx-1/https://grafana.com/blog/2024/07/23/how-to-set-up-grafana-mimir-using-ansible/https://developers.redhat.com/articles/2024/04/15/patch-updates-rhel-servers-ansible-automation-platform-24https://www.dbi-services.com/blog/ansible-loops-a-guide-from-basic-to-advanced-examples/https://github.com/bpbpublications/Multi-Cloud-Automation-with-Ansiblehttps://network-insight.net/2022/07/21/ansible-architecture-ansible-automation/https://www.digitalocean.com/community/cheatsheets/how-to-use-ansible-cheat-sheet-guidehttps://spacelift.io/blog/ansible-tutorialhttps://github.com/ansible-semaphore/semaphorehttps://www.rundeck.com/community-downloadshttps://raygun.com/blog/best-devops-tools/https://safiakhatoon.hashnode.dev/ansible-tutorial-basic-to-advanced