Security tips for VPN
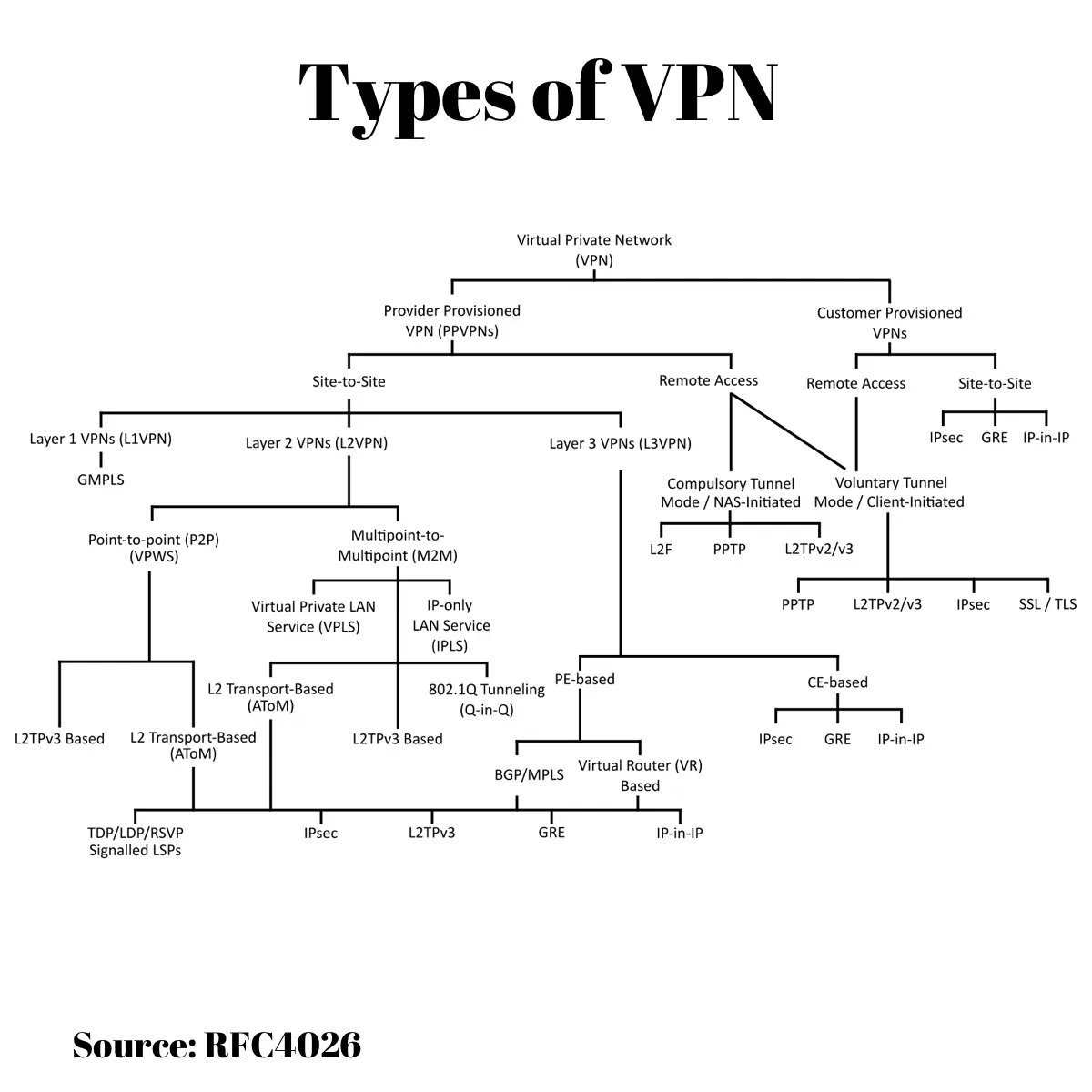
Types of VPN
Remote Access VPN
Remote Access VPN is the most common type of VPN used by individuals and small businesses. It allows users to access a private network securely from remote locations, such as a home office or a coffee shop. Remote Access VPN uses a client-server architecture that requires the user to install a VPN client software on their device, which then connects to a VPN server located on the private network. The user can then access resources on the private network as if they were physically present on the network. Remote Access VPN is ideal for telecommuting and mobile workers.
Site-to-Site VPN
Site-to-Site VPN, also known as Router-to-Router VPN, connects two or more private networks over the internet. It allows organizations to connect their different branch offices or data centers securely. Site-to-Site VPN uses a gateway device, such as a router or firewall, to establish a secure connection between the private networks. The gateway device encrypts the data that is transmitted between the two networks, ensuring that it is protected from unauthorized access. Site-to-Site VPN is ideal for large organizations with multiple locations.
Cloud VPN
Cloud VPN is a type of VPN that enables users to access cloud-based resources securely. Cloud VPN is hosted on a cloud service provider’s infrastructure and can be accessed from anywhere in the world. It provides a secure and reliable way for users to access cloud resources, such as virtual machines, storage, and applications. Cloud VPN uses encryption and tunneling protocols to ensure that data is transmitted securely between the user’s device and the cloud provider’s infrastructure. Cloud VPN is ideal for businesses that use cloud-based resources.
Security Tips
- Use a reputable VPN provider: Not all VPN services are created equal. It’s important to choose a provider with a good reputation and a strong track record of protecting user privacy. Look for VPNs that have been independently audited and have a clear and transparent privacy policy.
- Enable two-factor authentication: Two-factor authentication adds an additional layer of security to your VPN login process. In addition to entering your password, you’ll need to provide a second form of verification, such as a code sent to your phone or email. This makes it much harder for hackers to gain access to your VPN account.
- Always use the latest version of VPN software: VPN providers regularly release updates to fix security vulnerabilities and improve performance. Make sure you’re running the latest version of your VPN software to ensure you’re getting the most up-to-date security features.
- Use a strong and unique password: Your VPN password should be long, complex, and unique to your VPN account. Avoid using the same password for multiple accounts, and never use a password that’s easy to guess or commonly used.
- Avoid using free VPN services: Free VPN services often come with hidden costs, such as selling your data to third-party advertisers. If you’re serious about security, it’s worth paying for a reliable VPN service that puts your privacy first.
- Disable WebRTC to prevent IP leaks: WebRTC is a popular technology used by browsers to enable real-time communication between users. Unfortunately, it can also leak your real IP address, even if you’re using a VPN. Make sure to disable WebRTC in your browser settings to prevent this from happening.
- Turn off your VPN when not in use: While it’s important to use a VPN when accessing sensitive information, it’s not always necessary to have it running. In fact, some sites may actually block VPNs, preventing you from accessing certain content. If you’re not actively using your VPN, consider turning it off to conserve bandwidth and avoid potential issues.
- Use a VPN kill switch: A VPN kill switch is a feature that automatically shuts down your internet connection if your VPN connection drops. This prevents your traffic from leaking out onto the open internet, which could compromise your privacy and security.
- Avoid using public Wi-Fi hotspots: Public Wi-Fi networks are notoriously insecure, and should be avoided whenever possible. If you must use a public hotspot, make sure to connect through your VPN to protect your traffic from prying eyes.
- Always encrypt your sensitive data: When using a VPN, it’s important to make sure all of your sensitive data is properly encrypted. This includes things like your login credentials, financial information, and personal messages. Make sure you’re using end-to-end encryption whenever possible to keep your data safe from prying eyes.